Natural history of experimental coronary atherosclerosis and vascular remodeling in relation to endothelial shear stress: a serial, in vivo intravascular ultrasound study
- PMID: 20439786
- PMCID: PMC2902864
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.109.901678
Natural history of experimental coronary atherosclerosis and vascular remodeling in relation to endothelial shear stress: a serial, in vivo intravascular ultrasound study
Abstract
Background: The natural history of heterogeneous atherosclerotic plaques and the role of local hemodynamic factors throughout their development are unknown. We performed a serial study to assess the role of endothelial shear stress (ESS) and vascular remodeling in the natural history of coronary atherosclerosis.
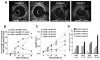
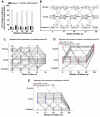
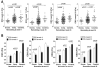
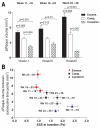
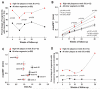
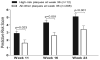
Methods and results: Intravascular ultrasound-based 3-dimensional reconstruction of all major coronary arteries (n=15) was performed serially in vivo in 5 swine 4, 11, 16, 23, and 36 weeks after induction of diabetes mellitus and hyperlipidemia. The reconstructed arteries were divided into 3-mm-long segments (n=304). ESS was calculated in all segments at all time points through the use of computational fluid dynamics. Vascular remodeling was assessed at each time point in all segments containing significant plaque, defined as maximal intima-media thickness >/=0.5 mm, at week 36 (n=220). Plaque started to develop at week 11 and progressively advanced toward heterogeneous, multifocal lesions at all subsequent time points. Low ESS promoted the initiation and subsequent progression of plaques. The local remodeling response changed substantially over time and determined future plaque evolution. Excessive expansive remodeling developed in regions of very low ESS, further exacerbated the low ESS, and was associated with the most marked plaque progression. The combined assessment of ESS, remodeling, and plaque severity enabled the early identification of plaques that evolved to high-risk lesions at week 36.
Conclusions: The synergistic effect of local ESS and the remodeling response to plaque formation determine the natural history of individual lesions. Combined in vivo assessment of ESS and remodeling may predict the focal formation of high-risk coronary plaque.
Figures
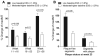
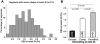
References
-
- Chatzizisis YS, Coskun AU, Jonas M, Edelman ER, Feldman CL, Stone PH. Role of endothelial shear stress in the natural history of coronary atherosclerosis and vascular remodeling: molecular, cellular and vascular behavior. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2007;49:2379–2393. - PubMed
-
- Cheruvu PK, Finn AV, Gardner C, Caplan J, Goldstein J, Stone GW, Virmani R, Muller JE. Frequency and distribution of thin-cap fibroatheroma and ruptured plaques in human coronary arteries: a pathologic study. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2007;50:940–949. - PubMed
-
- Chatzizisis YS, Jonas M, Coskun AU, Beigel R, Stone BV, Maynard C, Gerrity RS, Daley W, Rogers C, Edelman ER, Feldman CL, Stone PH. Prediction of the localization of high risk coronary atherosclerotic plaques on the basis of low endothelial shear stress: an intravascular ultrasound and histopathology natural history study. Circulation. 2008;117:993–1002. - PubMed
-
- Stone PH, Coskun AU, Kinlay S, Popma JJ, Sonka M, Wahle A, Yeghiazarians Y, Maynard C, Kuntz RE, Feldman CL. Regions of low endothelial shear stress are sites where coronary plaque progress and vascular remodeling occurs in humans: an in-vivo serial study. Eur Heart J. 2007;28:705–710. - PubMed
-
- von Birgelen C, Hartmann M, Mintz GS, Böse D, Eggebrecht H, Neumann T, Gössl M, Wieneke H, Schmermund A, Stoel MG, Verhorst PM, Erbel R. Remodeling index compared to actual vascular remodeling in atherosclerotic left main coronary arteries as assessed with long-term (> or =12 months) serial intravascular ultrasound. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2006;47:1363–1368. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

