Mexiletine is an effective antimyotonia treatment in myotonic dystrophy type 1
- PMID: 20439846
- PMCID: PMC2871004
- DOI: 10.1212/WNL.0b013e3181dc1a3a
Mexiletine is an effective antimyotonia treatment in myotonic dystrophy type 1
Abstract
Objective: To determine if mexiletine is safe and effective in reducing myotonia in myotonic dystrophy type 1 (DM1).
Background: Myotonia is an early, prominent symptom in DM1 and contributes to decreased dexterity, gait instability, difficulty with speech/swallowing, and muscle pain. A few preliminary trials have suggested that the antiarrhythmic drug mexiletine is useful, symptomatic treatment for nondystrophic myotonic disorders and DM1.
Methods: We performed 2 randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled crossover trials, each involving 20 ambulatory DM1 participants with grip or percussion myotonia on examination. The initial trial compared 150 mg of mexiletine 3 times daily to placebo, and the second trial compared 200 mg of mexiletine 3 times daily to placebo. Treatment periods were 7 weeks in duration separated by a 4- to 8-week washout period. The primary measure of myotonia was time for isometric grip force to relax from 90% to 5% of peak force after a 3-second maximum grip contraction. EKG measurements and adverse events were monitored in both trials.
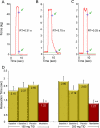
Results: There was a significant reduction in grip relaxation time with both 150 and 200 mg dosages of mexiletine. Treatment with mexiletine at either dosage was not associated with any serious adverse events, or with prolongation of the PR or QTc intervals or of QRS duration. Mild adverse events were observed with both placebo and mexiletine treatment.
Conclusions: Mexiletine at dosages of 150 and 200 mg 3 times daily is effective, safe, and well-tolerated over 7 weeks as an antimyotonia treatment in DM1.
Classification of evidence: This study provides Class I evidence that mexiletine at dosages of 150 and 200 mg 3 times daily over 7 weeks is well-tolerated and effective in reducing handgrip relaxation time in DM1.
Figures
Comment in
-
Mexiletine is an effective antimyotonia treatment in myotonic dystrophy type 1.Neurology. 2011 Jan 25;76(4):409; author reply 409. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0b013e3181fe72d7. Neurology. 2011. PMID: 21263144 No abstract available.
References
-
- Fu YH, Pizzuti A, Fenwick RG, et al. An unstable triplet repeat in a gene related to myotonic muscular dystrophy. Science 1992;255:1256–1258. - PubMed
-
- Harper PS. Myotonic Dystrophy, 3rd ed. London: WB Saunders; 2001.
-
- Moxley RT III. Myotonic Dystrophy: Handbook of Clinical Neurology. New York: Elsevier Science; 1992: 209–259.
-
- Leyburn P, Walton JN. The treatment of myotonia: a controlled clinical trial. Brain 1959;82:81–91. - PubMed
-
- Wolf A. Quinine: an effective form of treatment of myotonia. Arch Neurol Psychiatry 1936;36:382–384.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- FD-R-001662/FD/FDA HHS/United States
- 2 R01 AR049077/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- NS49639/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- U54NS48843/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR00044/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- RR24160/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- NS46487/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- HD44430/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- AR48143/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- 9 U54NS48843/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- NS50095/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- 1UL 1RR02416002/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- NS45686/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- DE16280/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- N01-AR-0-2250/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- NS58259/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- AR49077/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR49077/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- AR046806/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- K24 AR048143/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- AR049077/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- NS048843/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- 5 MO1 RR00044/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- N01-AR-5-2274/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- AR52274/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- NS50573/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- HL80107/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- NS42372/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024160/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- NS48843/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- NS52619/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- 1 R13 NS066630-01/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
