Estimating absolute and relative physical activity intensity across age via accelerometry in adults
- PMID: 20440028
- PMCID: PMC3292194
- DOI: 10.1123/japa.18.2.158
Estimating absolute and relative physical activity intensity across age via accelerometry in adults
Abstract
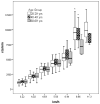
This study examined the predictive validity of accelerometers (ACC) to estimate physical activity intensity (PAI) across age and differences in intensity predictions when expressed in relative and absolute PAI terms. Ninety adults categorized into 3 age groups (20-29, 40-49, and 60-69 yr) completed a treadmill calibration study with simultaneous ACC (7164 Actigraph) and oxygen-consumption assessment. Results revealed strong linear relations between ACC output and measured PAI (R2 = .62-.89) across age and similar ACC cut-point ranges across age delineating absolute PAI ranges compared with previous findings. Comparing measured metabolic equivalents (METs) with estimated METs derived from previously published regression equations revealed that age did not affect predictive validity of ACC estimates of absolute PAI. Comparing ACC output expressed in relative vs. absolute terms across age revealed substantial differences in PAI ACC count ranges. Further work is warranted to increase the applicability ofACC use relative to PAI differences associated with physiological changes with age.
Figures
References
-
- Ainsworth BE, Bassett DR, Jr, Strath SJ, Swartz AM, O’Brien WL, Thompson RW, et al. Comparison of three methods for measuring the time spent in physical activity. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise. 2000;32(9 Suppl):S457–S464. - PubMed
-
- Ainsworth BE, Haskell WL, Leon AS, Jacobs DR, Jr, Montoye HJ, Sallis JF, et al. Compendium of physical activities: Classification of energy costs of human physical activities. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise. 1993;25(1):71–80. - PubMed
-
- American College of Sports Medicine. ACSM’s guidelines for exercise testing and prescription. 7. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2006.
-
- Bassett DR, Jr, Howley ET, Thompson DL, King GA, Strath SJ, McLaughlin JE, et al. Validity of inspiratory and expiratory methods of measuring gas exchange with a computerized system. Journal of Applied Physiology. 2001;91(1):218–224. - PubMed
-
- Bassett DR., Jr Validity and reliability issues in objective monitoring of physical activity. Research Quarterly for Exercise and Sport. 2000;71(2, Suppl):S30–S36. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

