Cancer-selective apoptotic effects of extracellular and intracellular Par-4
- PMID: 20440265
- PMCID: PMC2900490
- DOI: 10.1038/onc.2010.141
Cancer-selective apoptotic effects of extracellular and intracellular Par-4
Abstract
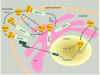
Selectivity toward cancer cells is the most desirable element in cancer therapeutics. Par-4 is a cancer cell-selective proapoptotic protein that functions intracellularly in the cytoplasmic and nuclear compartments as a tumor suppressor. Moreover, recent findings indicate that the Par-4 protein is secreted by cells, and extracellular Par-4 induces cancer cell-specific apoptosis by interaction with the cell-surface receptor GRP78. This review describes the mechanisms underlying the apoptotic effects of both extracellular and intracellular Par-4 acting through its effector domain SAC.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Systemic Par-4 inhibits non-autochthonous tumor growth.Cancer Biol Ther. 2011 Jul 15;12(2):152-7. doi: 10.4161/cbt.12.2.15734. Epub 2011 Jul 15. Cancer Biol Ther. 2011. PMID: 21613819 Free PMC article.
-
Cancer-selective apoptosis by tumor suppressor par-4.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2014;818:155-66. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4471-6458-6_7. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2014. PMID: 25001535 Review.
-
Novel mechanism of apoptosis resistance in cancer mediated by extracellular PAR-4.Cancer Res. 2013 Jan 15;73(2):1011-9. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-3212. Epub 2012 Nov 30. Cancer Res. 2013. PMID: 23204231 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of apoptosis by the tumor suppressor Par-4.J Cell Physiol. 2012 Dec;227(12):3715-21. doi: 10.1002/jcp.24098. J Cell Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22552839 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Par-4-GRP78 TRAIL, more twists and turns.Cancer Biol Ther. 2009 Nov;8(22):2103-5. doi: 10.4161/cbt.8.22.10140. Epub 2009 Nov 20. Cancer Biol Ther. 2009. PMID: 19823030 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
pH-Induced Folding of the Caspase-Cleaved Par-4 Tumor Suppressor: Evidence of Structure Outside of the Coiled Coil Domain.Biomolecules. 2018 Dec 4;8(4):162. doi: 10.3390/biom8040162. Biomolecules. 2018. PMID: 30518159 Free PMC article.
-
Crizotinib induces Par-4 secretion from normal cells and GRP78 expression on the cancer cell surface for selective tumor growth inhibition.Am J Cancer Res. 2023 Mar 15;13(3):976-991. eCollection 2023. Am J Cancer Res. 2023. PMID: 37034206 Free PMC article.
-
Neoadjuvant administration of hydroxychloroquine in a phase 1 clinical trial induced plasma Par-4 levels and apoptosis in diverse tumors.Genes Cancer. 2018 May;9(5-6):190-197. doi: 10.18632/genesandcancer.181. Genes Cancer. 2018. PMID: 30603055 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor Suppressor Par-4 Regulates Complement Factor C3 and Obesity.Front Oncol. 2022 Mar 29;12:860446. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.860446. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35425699 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic Par-4 inhibits non-autochthonous tumor growth.Cancer Biol Ther. 2011 Jul 15;12(2):152-7. doi: 10.4161/cbt.12.2.15734. Epub 2011 Jul 15. Cancer Biol Ther. 2011. PMID: 21613819 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahmed MM, Sheldon D, Fruitwala MA, Venkatasubbarao K, Lee EY, Gupta S, et al. Downregulation of PAR-4, a pro-apoptotic gene, in pancreatic tumors harboring K-ras mutation. Int J Cancer. 2008;122:63–70. - PubMed
-
- Almoguera C, Shibata D, Forrester K, Martin J, Arnheim N, Perucho M. Most human carcinomas of the exocrine pancreas contain mutant c-K-ras genes. Cell. 1988;53:549–554. - PubMed
-
- Barkett M, Gilmore TD. Control of apoptosis by Rel/NF-kappaB transcription factors. Oncogene. 1999;18:6910–6924. - PubMed
-
- Boghaert ER, Sells SF, Walid AJ, Malone P, Williams NM, Weinstein MH, et al. Immunohistochemical analysis of the proapoptotic protein Par-4 in normal rat tissues. Cell Growth Differ. 1997;8:881–890. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

