Assembly dynamics and stability of the pneumococcal epsilon zeta antitoxin toxin (PezAT) system from Streptococcus pneumoniae
- PMID: 20442221
- PMCID: PMC2898450
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.126250
Assembly dynamics and stability of the pneumococcal epsilon zeta antitoxin toxin (PezAT) system from Streptococcus pneumoniae
Abstract
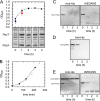
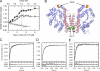
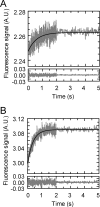
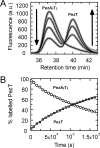
The pneumococcal epsilon zeta antitoxin toxin (PezAT) system is a chromosomally encoded, class II toxin antitoxin system from the human pathogen Streptococcus pneumnoniae. Neutralization of the bacteriotoxic protein PezT is carried out by complex formation with its cognate antitoxin PezA. Here we study the stability of the inhibitory complex in vivo and in vitro. We found that toxin release is impeded in Escherichia coli and Bacillus subtilis due to the proteolytic resistance of PezA once bound to PezT. These findings are supported by in vitro experiments demonstrating a strong thermodynamic stabilization of both proteins upon binding. A detailed kinetic analysis of PezAT assembly revealed that these particular features of PezAT are based on a strong, electrostatically guided binding mechanism leading to a stable toxin antitoxin complex with femtomolar affinity. Our data show that PezAT complex formation is distinct to all other conventional toxin antitoxin modules and a controlled mode of toxin release is required for activation.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Molecular and structural characterization of the PezAT chromosomal toxin-antitoxin system of the human pathogen Streptococcus pneumoniae.J Biol Chem. 2007 Jul 6;282(27):19606-18. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M701703200. Epub 2007 May 8. J Biol Chem. 2007. PMID: 17488720
-
The Streptococcus pneumoniae pezAT Toxin-Antitoxin System Reduces β-Lactam Resistance and Genetic Competence.Front Microbiol. 2016 Aug 25;7:1322. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2016.01322. eCollection 2016. Front Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27610103 Free PMC article.
-
Type II bacterial toxin-antitoxins: hypotheses, facts, and the newfound plethora of the PezAT system.FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2023 Sep 5;47(5):fuad052. doi: 10.1093/femsre/fuad052. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2023. PMID: 37715317 Free PMC article.
-
ε/ζ systems: their role in resistance, virulence, and their potential for antibiotic development.J Mol Med (Berl). 2011 Dec;89(12):1183-94. doi: 10.1007/s00109-011-0797-4. Epub 2011 Aug 6. J Mol Med (Berl). 2011. PMID: 21822621 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Toxin-antitoxin genes of the Gram-positive pathogen Streptococcus pneumoniae: so few and yet so many.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2012 Dec;76(4):773-91. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00030-12. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2012. PMID: 23204366 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Prokaryote toxin-antitoxin modules: Complex regulation of an unclear function.Protein Sci. 2021 Jun;30(6):1103-1113. doi: 10.1002/pro.4071. Epub 2021 Apr 7. Protein Sci. 2021. PMID: 33786944 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dynamics-Based Regulatory Switches of Type II Antitoxins: Insights into New Antimicrobial Discovery.Antibiotics (Basel). 2023 Mar 23;12(4):637. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics12040637. Antibiotics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37106997 Free PMC article.
-
Conformational change as a mechanism for toxin activation in bacterial toxin-antitoxin systems.J Virol. 2024 Nov 19;98(11):e0151324. doi: 10.1128/jvi.01513-24. Epub 2024 Oct 24. J Virol. 2024. PMID: 39445801 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of Three Type II Toxin-Antitoxin Systems in Streptococcus suis Serotype 2.Toxins (Basel). 2018 Nov 13;10(11):467. doi: 10.3390/toxins10110467. Toxins (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30428568 Free PMC article.
-
A novel mechanism of programmed cell death in bacteria by toxin-antitoxin systems corrupts peptidoglycan synthesis.PLoS Biol. 2011 Mar;9(3):e1001033. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1001033. Epub 2011 Mar 22. PLoS Biol. 2011. PMID: 21445328 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

