An IV for the RCT: using instrumental variables to adjust for treatment contamination in randomised controlled trials
- PMID: 20442226
- PMCID: PMC3230230
- DOI: 10.1136/bmj.c2073
An IV for the RCT: using instrumental variables to adjust for treatment contamination in randomised controlled trials
Abstract
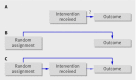
Although the randomised controlled trial is the "gold standard" for studying the efficacy and safety of medical treatments, it is not necessarily free from bias. When patients do not follow the protocol for their assigned treatment, the resultant "treatment contamination" can produce misleading findings. The methods used historically to deal with this problem, the "as treated" and "per protocol" analysis techniques, are flawed and inaccurate. Intention to treat analysis is the solution most often used to analyse randomised controlled trials, but this approach ignores this issue of treatment contamination. Intention to treat analysis estimates the effect of recommending a treatment to study participants, not the effect of the treatment on those study participants who actually received it. In this article, we describe a simple yet rarely used analytical technique, the "contamination adjusted intention to treat analysis," which complements the intention to treat approach by producing a better estimate of the benefits and harms of receiving a treatment. This method uses the statistical technique of instrumental variable analysis to address contamination. We discuss the strengths and limitations of the current methods of addressing treatment contamination and the contamination adjusted intention to treat technique, provide examples of effective uses, and discuss how using estimates generated by contamination adjusted intention to treat analysis can improve clinical decision making and patient care.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: Both authors have completed the Unified Competing Interest form at
Figures
References
-
- Schroder FH, Hugosson J, Roobol MJ, Tammela TL, Ciatto S, Nelen V, et al. Screening and prostate-cancer mortality in a randomized European study. N Engl J Med 2009;360:1320-8. - PubMed
-
- Calverley PM, Anderson JA, Celli B, Ferguson GT, Jenkins C, Jones PW, et al. Salmeterol and fluticasone propionate and survival in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. N Engl J Med 2007;356:775-89. - PubMed
-
- Packer M, Fowler MB, Roecker EB, Coats AJ, Katus HA, Krum H, et al. Effect of carvedilol on the morbidity of patients with severe chronic heart failure: results of the carvedilol prospective randomized cumulative survival (COPERNICUS) study. Circulation 2002;106:2194-9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
