Bortezomib sensitizes human renal cell carcinomas to TRAIL apoptosis through increased activation of caspase-8 in the death-inducing signaling complex
- PMID: 20442297
- PMCID: PMC2873082
- DOI: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-10-0022
Bortezomib sensitizes human renal cell carcinomas to TRAIL apoptosis through increased activation of caspase-8 in the death-inducing signaling complex
Abstract
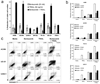
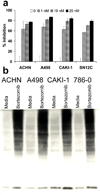
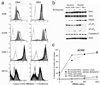
Bortezomib (VELCADE) could sensitize certain human renal cell carcinoma (RCC) lines to the apoptotic effects of tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL). Analysis of seven human RCC showed a clear increase in the sensitivity of four of the RCC to TRAIL cytotoxicity following bortezomib (5-20 nmol/L) treatment, whereas the remaining three remained resistant. Tumor cell death following sensitization had all the features of apoptosis. The enhanced antitumor activity of the bortezomib and TRAIL combination was confirmed in long-term (6 days) cancer cell outgrowth assays. The extent of proteasome inhibition by bortezomib in the various RCC was equivalent. Following bortezomib treatment, neither changes in the intracellular protein levels of various Bcl-2 and IAP family members, nor minor changes in expression of TRAIL receptors (DR4, DR5), correlated well with the sensitization or resistance of RCC to TRAIL-mediated apoptosis. However, enhanced procaspase-8 activation following bortezomib pretreatment and subsequent TRAIL exposure was only observed in the sensitized RCC in both cell extracts and death-inducing signaling complex immunoprecipitates. These data suggest that the molecular basis for bortezomib sensitization of RCC to TRAIL primarily involves early amplification of caspase-8 activity. In the absence of this increased caspase-8 activation, other bortezomib-induced changes are not sufficient to sensitize RCC to TRAIL-mediated apoptosis.
(c)2010 AACR.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Similar articles
-
Bortezomib sensitizes human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells to TRAIL-mediated apoptosis via activation of both extrinsic and intrinsic apoptosis pathways.Mol Cancer Ther. 2010 Jun;9(6):1842-51. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-09-0918. Epub 2010 Jun 1. Mol Cancer Ther. 2010. PMID: 20515944 Free PMC article.
-
Treating metastatic solid tumors with bortezomib and a tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand receptor agonist antibody.J Natl Cancer Inst. 2008 May 7;100(9):649-62. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djn113. Epub 2008 Apr 29. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2008. PMID: 18445820 Free PMC article.
-
Bortezomib sensitises TRAIL-resistant HPV-positive head and neck cancer cells to TRAIL through a caspase-dependent, E6-independent mechanism.Cell Death Dis. 2014 Oct 23;5(10):e1489. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2014.455. Cell Death Dis. 2014. PMID: 25341043 Free PMC article.
-
Combining proteasome inhibition with TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (Apo2L/TRAIL) for cancer therapy.Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2006 Jan;55(1):76-84. doi: 10.1007/s00262-005-0676-3. Epub 2005 Oct 27. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2006. PMID: 15864587 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bortezomib and TRAIL: a perfect match for apoptotic elimination of tumour cells?Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2013 Mar;85(3):363-72. doi: 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2012.08.001. Epub 2012 Sep 1. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2013. PMID: 22944363 Review.
Cited by
-
Development of Proteasome Inhibitors as Therapeutic Drugs.J Clin Cell Immunol. 2012 Mar 15;S5:5. doi: 10.4172/2155-9899.s5-005. J Clin Cell Immunol. 2012. PMID: 23338480 Free PMC article.
-
Immune-Based and Novel Therapies in Variant Histology Renal Cell Carcinomas.Cancers (Basel). 2025 Jan 20;17(2):326. doi: 10.3390/cancers17020326. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39858107 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NF-κB inhibition by bortezomib permits IFN-γ-activated RIP1 kinase-dependent necrosis in renal cell carcinoma.Mol Cancer Ther. 2013 Aug;12(8):1568-78. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-12-1010. Epub 2013 May 8. Mol Cancer Ther. 2013. PMID: 23657944 Free PMC article.
-
Phase II open-label study of recombinant circularly permuted TRAIL as a single-agent treatment for relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma.Chin J Cancer. 2016 Sep 8;35(1):86. doi: 10.1186/s40880-016-0140-0. Chin J Cancer. 2016. PMID: 27608772 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Review on Bortezomib Resistance in Multiple Myeloma and Potential Role of Emerging Technologies.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Jan 12;16(1):111. doi: 10.3390/ph16010111. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36678608 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Adams J. The development of proteasome inhibitors as anticancer drugs. Cancer Cell. 2004;5:417–421. - PubMed
-
- Mitsiades CS, Treon SP, Mitsiades N, et al. TRAIL/Apo2L ligand selectively induces apoptosis and overcomes drug resistance in multiple myeloma: therapeutic applications. Blood. 2001;98:795–804. - PubMed
-
- Sayers TJ, Brooks AD, Koh CY, et al. The proteasome inhibitor PS-341 sensitizes neoplastic cells to TRAIL-mediated apoptosis by reducing levels of c-FLIP. Blood. 2003;102:303–310. - PubMed
-
- Johnson TR, Stone K, Nikrad M, et al. The proteasome inhibitor PS-341 overcomes TRAIL resistance in Bax and caspase 9-negative or Bcl-xL overexpressing cells. Oncogene. 2003;22:4953–4963. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

