Molecular imaging of atherosclerotic plaques targeted to oxidized LDL receptor LOX-1 by SPECT/CT and magnetic resonance
- PMID: 20442371
- PMCID: PMC2955298
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCIMAGING.109.896654
Molecular imaging of atherosclerotic plaques targeted to oxidized LDL receptor LOX-1 by SPECT/CT and magnetic resonance
Abstract
Background: The oxidized low-density lipoprotein receptor (LDLR) LOX-1 plays a crucial role in atherosclerosis. We sought to detect and assess atherosclerotic plaque in vivo by using single-photon emission computed tomography/computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging and a molecular probe targeted at LOX-1.
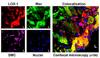
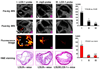
Methods and results: Apolipoprotein E(-/-) mice fed a Western diet and LDLR(-/-) and LDLR(-/-)/LOX-1(-/-) mice fed an atherogenic diet were used. Imaging probes consisted of liposomes decorated with anti-LOX-1 antibodies or nonspecific immunoglobulin G, (111)indium or gadolinium, and 1,1'-dioctadecyl-3,3,3',3'-tetramethylindocarbocyanine fluorescence markers. In vivo imaging was performed 24 hours after intravenous injection (150 microL) of LOX-1 or nonspecific immunoglobulin G probes labeled with either (111)indium (600 muCi) or gadolinium (0.075 mmol/kg), followed by aortic excision for phosphor imaging and Sudan IV staining, or fluorescence imaging and hematoxylin/eosin staining. The LOX-1 probe also colocalized with specific cell types, apoptosis, and matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression in frozen aortic sections. Single-photon emission computed tomography/computed tomography imaging of the LOX-1 probe showed aortic arch "hot spots" in apolipoprotein E(-/-) mice (n=8), confirmed by phosphor imaging. Magnetic resonance imaging showed significant Gd enhancement in atherosclerotic plaques in LDLR(-/-) mice with the LOX-1 (n=7) but not with the nonspecific immunoglobulin G (n=5) probe. No signal enhancement was observed in LDLR(-/-)/LOX-1(-/-) mice injected with the LOX-1 probe (n=5). These results were confirmed by ex vivo fluorescence imaging. The LOX-1 probe bound preferentially to the plaque shoulder, a region with vulnerable plaque features, including extensive LOX-1 expression, macrophage accumulation, apoptosis, and matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression.
Conclusions: LOX-1 can be used as a target for molecular imaging of atherosclerotic plaque in vivo. Furthermore, the LOX-1 imaging signal is associated with markers of rupture-prone atherosclerotic plaque.
Figures





References
-
- Mehta JL, Chen J, Hermonat PL, Romeo F, Novelli G. Lectin-like, oxidized low-density lipoprotein receptor-1 (LOX-1): a critical player in the development of atherosclerosis and related disorders. Cardiovasc Res. 2006;69:36–45. - PubMed
-
- Sawamura T, Kume N, Aoyama T, et al. An endothelial receptor for oxidized low-density lipoprotein. Nature. 1997;386:73–77. - PubMed
-
- Cominacini L, Pasini AF, Garbin U, et al. Oxidized low density lipoprotein (ox-LDL) binding to ox-LDL receptor-1 in endothelial cells induces the activation of NF-κB through an increased production of intracellular reactive oxygen species. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:12633–12638. - PubMed
-
- Li D, Mehta JL. Upregulation of endothelial receptor for oxidized LDL (LOX-1) by oxidized LDL and implications in apoptosis of human coronary artery endothelial cells: evidence from use of antisense LOX-1 mRNA and chemical inhibitors. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2000;20:1116–1122. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

