Adipocytokine orosomucoid integrates inflammatory and metabolic signals to preserve energy homeostasis by resolving immoderate inflammation
- PMID: 20442402
- PMCID: PMC2903347
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.085464
Adipocytokine orosomucoid integrates inflammatory and metabolic signals to preserve energy homeostasis by resolving immoderate inflammation
Abstract
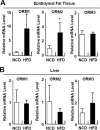
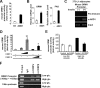
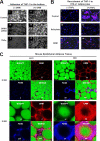
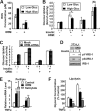
Orosomucoid (ORM), also called alpha-1 acid glycoprotein, is an abundant plasma protein that is an immunomodulator induced by stressful conditions such as infections. In this study, we reveal that Orm is induced selectively in the adipose tissue of obese mice to suppress excess inflammation that otherwise disturbs energy homeostasis. Adipose Orm levels were elevated by metabolic signals, including insulin, high glucose, and free fatty acid, as well as by the proinflammatory cytokine tumor necrosis factor-alpha, which is found in increased levels in the adipose tissue of morbid obese subjects. In both adipocytes and macrophages, ORM suppressed proinflammatory gene expression and pathways such as NF-kappaB and mitogen-activated protein kinase signalings and reactive oxygen species generation. Concomitantly, ORM relieved hyperglycemia-induced insulin resistance as well as tumor necrosis factor-alpha-mediated lipolysis in adipocytes. Accordingly, ORM improved glucose and insulin tolerance in obese and diabetic db/db mice. Taken together, our results suggest that ORM integrates inflammatory and metabolic signals to modulate immune responses to protect adipose tissue from excessive inflammation and thereby from metabolic dysfunction.
Figures




References
-
- Hotamisligil G. S. (2006) Nature 444, 860–867 - PubMed
-
- Hotamisligil G. S., Shargill N. S., Spiegelman B. M. (1993) Science 259, 87–91 - PubMed
-
- Suganami T., Tanimoto-Koyama K., Nishida J., Itoh M., Yuan X., Mizuarai S., Kotani H., Yamaoka S., Miyake K., Aoe S., Kamei Y., Ogawa Y. (2007) Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 27, 84–91 - PubMed
-
- Zhang H. H., Halbleib M., Ahmad F., Manganiello V. C., Greenberg A. S. (2002) Diabetes 51, 2929–2935 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

