L-methionine decreases dendritic spine density in mouse frontal cortex
- PMID: 20442623
- PMCID: PMC2882068
- DOI: 10.1097/WNR.0b013e3283373126
L-methionine decreases dendritic spine density in mouse frontal cortex
Abstract
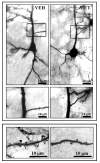
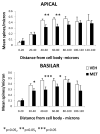
Schizophrenia postmortem brain is characterized by gamma aminobutyric acid downregulation and by decreased dendritic spine density in frontal cortex. Protracted L-methionine treatment exacerbates schizophrenia symptoms, and our earlier work (Tremolizzo et al. and Dong et al.) has shown that L-methionine decreases reelin and GAD67 transcription in mice which is prevented by co-administration of valproate. In this study, we observed a decrease in spine density following L-methionine treatment, which was prevented by co-administration of valproate. Together with our earlier findings conducted under the same experimental conditions, we suggest that downregulation of spine density in L-methionine-treated mice may be because of the decreased expression of reelin and that valproate may prevent spine downregulation by inhibiting the methylation induced decrease in reelin.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Valproate corrects the schizophrenia-like epigenetic behavioral modifications induced by methionine in mice.Biol Psychiatry. 2005 Mar 1;57(5):500-9. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2004.11.046. Biol Psychiatry. 2005. PMID: 15737665
-
[Epigenetic model in the pharmacologic modulation of vulnerability to schizophrenia].Encephale. 2007 Nov;33(Pt 3):867-9. doi: 10.1016/s0013-7006(07)92911-5. Encephale. 2007. PMID: 18402359 French. No abstract available.
-
An epigenetic mouse model for molecular and behavioral neuropathologies related to schizophrenia vulnerability.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002 Dec 24;99(26):17095-100. doi: 10.1073/pnas.262658999. Epub 2002 Dec 12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002. PMID: 12481028 Free PMC article.
-
Reelin down-regulation in mice and psychosis endophenotypes.Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2006;30(8):1065-77. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2006.04.001. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2006. PMID: 16769115 Review.
-
Dendritic spine hypoplasticity and downregulation of reelin and GABAergic tone in schizophrenia vulnerability.Neurobiol Dis. 2001 Oct;8(5):723-42. doi: 10.1006/nbdi.2001.0436. Neurobiol Dis. 2001. PMID: 11592844 Review.
Cited by
-
The dynamics of DNA methylation in schizophrenia and related psychiatric disorders.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2013 Jan;38(1):138-66. doi: 10.1038/npp.2012.125. Epub 2012 Sep 5. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2013. PMID: 22948975 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetic RELN Dysfunction in Schizophrenia and Related Neuropsychiatric Disorders.Front Cell Neurosci. 2016 Apr 5;10:89. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2016.00089. eCollection 2016. Front Cell Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27092053 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metabolomic and transcriptomic signatures of prenatal excessive methionine support nature rather than nurture in schizophrenia pathogenesis.Commun Biol. 2020 Jul 30;3(1):409. doi: 10.1038/s42003-020-01124-8. Commun Biol. 2020. PMID: 32732995 Free PMC article.
-
A neurochemical basis for an epigenetic vision of psychiatric disorders (1994-2009).Pharmacol Res. 2011 Oct;64(4):344-9. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2011.05.026. Epub 2011 Jun 15. Pharmacol Res. 2011. PMID: 21699980 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DNA methylation and demethylation as targets for antipsychotic therapy.Dialogues Clin Neurosci. 2014 Sep;16(3):419-29. doi: 10.31887/DCNS.2014.16.3/aguidotti. Dialogues Clin Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 25364290 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Glanz LA, Lewis DA. Decreased dendritic spine density on prefrontal cortical pyramidal neurons in schizophrenia. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2000;57:65–73. - PubMed
-
- Guidotti A, Auta J, Davis JM, DiGiorgi-Cerenini V, Dwivedi J, Grayson DR, et al. Decreased reelin and glutamic acid decarboxylase 67 (GAD67) expression in schizophrenia and bipolar disorders a postmortem brain study. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2000;57:1061–1069. - PubMed
-
- Ruzicka WB, Zhubi A, Veldic M, Grayson DR, Costa E, Guidotti A. Selective epigenetic alteration of layer 1 GABAergic neurons isolated from prefrontal cortex of schizophrenia patients using laser-assisted microdissection. Mol Psychiatry. 2007;12:385–397. - PubMed
-
- Levenson JM, Qiu S, Weeber EJ. The role of reelin in adult synaptic function and the genetic and epigenetic regulation of the reelin gene. Biochem Biophys Acta. 2008;1779:422–431. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

