RNA polymerase activity and specific RNA structure are required for efficient HCV replication in cultured cells
- PMID: 20442786
- PMCID: PMC2861710
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1000885
RNA polymerase activity and specific RNA structure are required for efficient HCV replication in cultured cells
Abstract
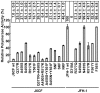
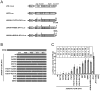
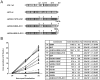
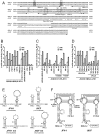
We have previously reported that the NS3 helicase (N3H) and NS5B-to-3'X (N5BX) regions are important for the efficient replication of hepatitis C virus (HCV) strain JFH-1 and viral production in HuH-7 cells. In the current study, we investigated the relationships between HCV genome replication, virus production, and the structure of N5BX. We found that the Q377R, A450S, S455N, R517K, and Y561F mutations in the NS5B region resulted in up-regulation of J6CF NS5B polymerase activity in vitro. However, the activation effects of these mutations on viral RNA replication and virus production with JFH-1 N3H appeared to differ. In the presence of the N3H region and 3' untranslated region (UTR) of JFH-1, A450S, R517K, and Y561F together were sufficient to confer HCV genome replication activity and virus production ability to J6CF in cultured cells. Y561F was also involved in the kissing-loop interaction between SL3.2 in the NS5B region and SL2 in the 3'X region. We next analyzed the 3' structure of HCV genome RNA. The shorter polyU/UC tracts of JFH-1 resulted in more efficient RNA replication than J6CF. Furthermore, 9458G in the JFH-1 variable region (VR) was responsible for RNA replication activity because of its RNA structures. In conclusion, N3H, high polymerase activity, enhanced kissing-loop interactions, and optimal viral RNA structure in the 3'UTR were required for J6CF replication in cultured cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Amino Acid Mutations in the NS4A Region of Hepatitis C Virus Contribute to Viral Replication and Infectious Virus Production.J Virol. 2017 Jan 31;91(4):e02124-16. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02124-16. Print 2017 Feb 15. J Virol. 2017. PMID: 27928005 Free PMC article.
-
The NS3 helicase and NS5B-to-3'X regions are important for efficient hepatitis C virus strain JFH-1 replication in Huh7 cells.J Virol. 2007 Aug;81(15):8030-40. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02088-06. Epub 2007 May 23. J Virol. 2007. PMID: 17522229 Free PMC article.
-
Production of infectious chimeric hepatitis C virus genotype 2b harboring minimal regions of JFH-1.J Virol. 2012 Feb;86(4):2143-52. doi: 10.1128/JVI.05386-11. Epub 2011 Dec 7. J Virol. 2012. PMID: 22156532 Free PMC article.
-
Form confers function: Case of the 3'X region of the hepatitis C virus genome.World J Gastroenterol. 2018 Aug 14;24(30):3374-3383. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i30.3374. World J Gastroenterol. 2018. PMID: 30122877 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targets for inhibition of hepatitis C virus replication.Antivir Ther. 1998;3(Suppl 3):83-91. Antivir Ther. 1998. PMID: 10726058 Review.
Cited by
-
Robust full-length hepatitis C virus genotype 2a and 2b infectious cultures using mutations identified by a systematic approach applicable to patient strains.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 May 1;109(18):E1101-10. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1203829109. Epub 2012 Mar 30. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012. PMID: 22467829 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of CCN1 via the 3'-untranslated region.J Cell Commun Signal. 2013 Aug;7(3):207-17. doi: 10.1007/s12079-013-0202-x. Epub 2013 May 16. J Cell Commun Signal. 2013. PMID: 23677691 Free PMC article.
-
Two crucial early steps in RNA synthesis by the hepatitis C virus polymerase involve a dual role of residue 405.J Virol. 2012 Jul;86(13):7107-17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00459-12. Epub 2012 Apr 24. J Virol. 2012. PMID: 22532694 Free PMC article.
-
A comprehensive structure-function comparison of hepatitis C virus strain JFH1 and J6 polymerases reveals a key residue stimulating replication in cell culture across genotypes.J Virol. 2011 Mar;85(6):2565-81. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02177-10. Epub 2011 Jan 5. J Virol. 2011. PMID: 21209117 Free PMC article.
-
Direct evidence for RNA-RNA interactions at the 3' end of the Hepatitis C virus genome using surface plasmon resonance.RNA. 2013 Jul;19(7):982-91. doi: 10.1261/rna.037606.112. Epub 2013 May 7. RNA. 2013. PMID: 23651615 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lemon S, Walker C, Alter M, Yi M. Hepatitis C virus. In: Knipe D, Howley P, editors. Fields Virology 5 ed. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott-Raven Publishers; 2007. pp. 1253–1304.
-
- Wasley A, Alter MJ. Epidemiology of hepatitis C: geographic differences and temporal trends. Semin Liver Dis. 2000;20:1–16. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

