Impact of Rituximab (Rituxan) on the Treatment of B-Cell Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma
- PMID: 20442809
- PMCID: PMC2844047
Impact of Rituximab (Rituxan) on the Treatment of B-Cell Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma
Abstract
Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma (NHL) is the most common hematological malignancy in adults, with B-cell lymphomas accounting for 85% of all NHLs. The most substantial advancement in the treatment of B-cell malignancies, since the advent of combination chemotherapy, has been the addition of the monoclonal anti-CD20 antibody rituximab (Rituxan). Since its initially reported single-agent activity in indolent lymphomas in 1997, the role of rituximab has expanded to cover both indolent and aggressive lymphomas.This article focuses on the impact of rituximab on the treatment, survival, and long-term outcomes of patients with indolent and aggressive lymphomas over the past two decades.
Keywords: non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma; rituximab.
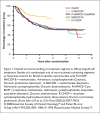
Figures
References
-
- Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E. Cancer statistics, 2008. CA Cancer J Clin. 2008;58(2):71–96. - PubMed
-
- Rudiger T, Muller-Hermelink HK. WHO classification of malignant lymphomas. Radiologe. 2002;42(12):936–942. - PubMed
-
- Harris NL, Jaffe ES, Diebold J, et al. The World Health Organization Classification of Neoplastic Diseases of the Hematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues. Report of the Clinical Advisory Committee meeting. Airlie House, Virginia, November 1997; Ann Oncol; 1999. pp. 1419–1432. - PubMed
-
- Armitage JO, Weisenburger DD. New approach to classifying non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas: Clinical features of the major histologic subtypes. Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma Classification Project. J Clin Oncol. 1998;16(8):2780–2795. - PubMed
-
- Tedder TF, Engel P. CD20: A regulator of cell–cycle progression of B lymphocytes. Immunol Today. 1994;15(9):450–454. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
