Disposition kinetics of sparfloxacin in healthy, hepatopathic, and nephropathic conditions in chicken after single intravenous administration
- PMID: 20442816
- PMCID: PMC2861809
- DOI: 10.4103/0253-7613.55204
Disposition kinetics of sparfloxacin in healthy, hepatopathic, and nephropathic conditions in chicken after single intravenous administration
Abstract
Objective: To study the variation of disposition kinetic values of sparfloxacin in healthy, hepatopathic, and nephropathic chickens after a single intravenous administration.
Materials and methods: Hepatotoxicity was induced by the administration of paracetamol (500 mg / kg / day, p.o. for seven days) and nephrotoxicity by uranyl nitrate (2.0 mg / kg / day dissolved in distilled water, i.v. for four days) in chickens. Disposition kinetic studies of sparfloxacin were investigated in healthy as well as hepatopathic and nephropathic birds after a single intravenous administration at 40 mg / kg body weight.
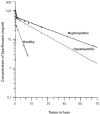
Results: Maximum plasma concentration detected at 0.16 hour was 31.25 +/- 2.95, 61.95 +/-1.85, and 99.86 +/- 2.21 mug / ml in healthy, hepatopathic, and nephropathic group, respectively. The drug could not be detected in the plasma of healthy birds beyond 12-hour period, while the same was detectable for 72 hour in the plasma of hepatopathic and nephropathic birds. The concentration of sparfloxacin was significantly (P < 0.01) higher in all the samples of hepathopathic and nephropathic birds compared to healthy birds. All the kinetic values were increased (P < 0.01) in the hepatopathic and nephropathic birds, except Vd(area) and Cl(B) values in hepatopathic Birds; while beta and Cl(B) values nephropathic birds were decreased significantly than that of healthy birds.
Conclusions: The dose of sparfloxacin may be reduced in hepatopathic as well as nephropathic birds.
Keywords: Birds; disposition kinetics; healthy; hepatopathic; nephropathic; sparfloxacin.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pharmacokinetics of ceftriaxone in carbontetrachloride-induced hepatopathic and uranyl nitrate-induced nephropathic goats following single dose intravenous administration.Drug Metab Lett. 2008 Jan;2(1):23-8. doi: 10.2174/187231208783478515. Drug Metab Lett. 2008. PMID: 19356066
-
Disposition kinetics of doxycycline in chickens naturally infected with Mycoplasma gallisepticum.Br Poult Sci. 2004 Aug;45(4):550-6. doi: 10.1080/00071660400001058. Br Poult Sci. 2004. PMID: 15484732
-
Tissue distribution and disposition kinetics of enrofloxacin in healthy and E. coli infected broilers.Dtsch Tierarztl Wochenschr. 2000 Jan;107(1):23-7. Dtsch Tierarztl Wochenschr. 2000. PMID: 10689795
-
Use of adductor pollicis muscle thickness in hospitalized or ambulatory patients: a systematic review.Rev Lat Am Enfermagem. 2018 Jun 21;26:e2960. doi: 10.1590/1518-8345.2045.2960. Rev Lat Am Enfermagem. 2018. PMID: 29947718 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical pharmacokinetics of sparfloxacin.Clin Pharmacokinet. 1993 Nov;25(5):358-69. doi: 10.2165/00003088-199325050-00002. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1993. PMID: 8287631 Review.
Cited by
-
Disposition of ceftriaxone in hepatopathic goats following single-intramuscular dosing.Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 2013 Dec;38(4):269-73. doi: 10.1007/s13318-013-0129-x. Epub 2013 Apr 4. Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 2013. PMID: 23553049
-
Comparative Pharmacokinetics of Levofloxacin in Healthy and Renal Damaged Muscovy Ducks following Intravenous and Oral Administration.Vet Med Int. 2014;2014:986806. doi: 10.1155/2014/986806. Epub 2014 Feb 4. Vet Med Int. 2014. PMID: 24707439 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shimada J, Nogita T, Ishifashi Y. Clinical pharmacokinetics of sparfloxacin. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1993;25:358–69. - PubMed
-
- Montay G. Pharmacokinetics of sparfloxacin in healthy volunteers and patients: a review. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1996;37:27–39. - PubMed
-
- Wise R, Honeybourne D. A review of the penetration of sparfloxacin into the lower respiratory tract and sinuses. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1996;37:57–63. - PubMed
-
- Juliet S, Baman A, Majumdar S, Mandal TK, Chakraborty Disposition kinetics of sulphamethoxy pyridazine during endotoxin induced fever and its modification by sodium salicylates in goats. Indian J Pharmacol. 1995;27:222–6.
-
- Datta B, Mandal TK, Chakraborty AK. Pharmacokinetics of cefotaxime in goats with experimentally induced kidney damage. Indian J Pharmacol. 2003;35:173–6.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources