Role of central muscarinic cholinergic receptors in the formalin-induced pain in rats
- PMID: 20442824
- PMCID: PMC2861817
- DOI: 10.4103/0253-7613.55205
Role of central muscarinic cholinergic receptors in the formalin-induced pain in rats
Abstract
Objectives: In the present study, central effects of physostigmine and atropine have investigated in the formalin-induced pain in rats.
Materials and methods: In conscious rats implanted with an intracerebroventricular (i.c.v.) cannula, the effects of i.c.v. injection of physostigmine and atropine were investigated on the formalin test in the rat. Formalin test was induced by subcutaneous (s.c.) injection of formalin (50 mul, 1%) in ventral surface of left hind paw, and durations of licking and biting of the injected paw were measured in 5-min blocks for 1 h.
Results: FORMALIN PRODUCED A BIPHASIC RESPONSE (FIRST PHASE: 0-5 and second phase: 15-40 min) in durations of licking and biting of the injected paw. Physostigmine at doses of 2.5, 5 and 10 ug significantly (P < 0.05) attenuated both first and second phases of pain response. Atropine (5 and 10 ug), used alone, produced no significant effect on pain, but pretreatment with atropine (10 ug) significantly (P < 0.05) blocked antinociception induced by physostigmine (5 ug).
Conclusion: These results indicate that i.c.v. physostigmine can affect both neurogenic and inflammatory phases of formalin-induced pain through a mechanism in which the muscarinic cholinergic receptors are involved.
Keywords: Atropine; brain; formalin-induced pain; physostigmine; rats.
Figures
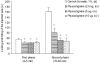
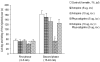
Similar articles
-
Effects of mepyramine and famotidine on the physostigmine-induced antinociception in the formalin test in rats.Pak J Biol Sci. 2008 Nov 15;11(22):2573-8. doi: 10.3923/pjbs.2008.2573.2578. Pak J Biol Sci. 2008. PMID: 19260335
-
Central effect of histamine and peripheral effect of histidine on the formalin-induced pain response in mice.Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2004 Aug;31(8):518-22. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1681.2004.04033.x. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2004. PMID: 15298544
-
Effect of pilocarpine on the formalin-induced orofacial pain in rats.Vet Res Forum. 2012 Spring;3(2):91-5. Vet Res Forum. 2012. PMID: 25653753 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of crocin on the morphine-induced antinociception in the formalin test in rats.Phytother Res. 2010 Mar;24(3):410-3. doi: 10.1002/ptr.2965. Phytother Res. 2010. PMID: 19653196
-
Effects of subcutaneous and intracerebroventricular injection of physostigmine on the acute corneal nociception in rats.Pharmacol Rep. 2010 Sep-Oct;62(5):858-63. doi: 10.1016/s1734-1140(10)70345-5. Pharmacol Rep. 2010. PMID: 21098868
Cited by
-
Methanol extract of Cola nitida ameliorates inflammation and nociception in experimental animals.Neurobiol Pain. 2019 Jan 21;5:100027. doi: 10.1016/j.ynpai.2019.100027. eCollection 2019 Jan-Jul. Neurobiol Pain. 2019. PMID: 31194116 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular, Cellular and Circuit Basis of Cholinergic Modulation of Pain.Neuroscience. 2018 Sep 1;387:135-148. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2017.08.049. Epub 2017 Sep 8. Neuroscience. 2018. PMID: 28890048 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Characterization of the Antinociceptive Mechanisms of Khat Extract (Catha edulis) in Mice.Front Neurol. 2017 Mar 2;8:69. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2017.00069. eCollection 2017. Front Neurol. 2017. PMID: 28316587 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of acetylcholine on pain-related electric activities in the hippocampal CA3 of rats.J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2011 Apr;118(4):555-61. doi: 10.1007/s00702-010-0545-x. Epub 2011 Jan 19. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2011. PMID: 21246223
-
Effects of Hydroalcoholic Extract of Tanacetum Sonbolii (Asteraceae) on Pain-related Behaviors during Formalin Test in Mice.Basic Clin Neurosci. 2014 Spring;5(2):162-8. Basic Clin Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 25337375 Free PMC article.
References
-
- File SE, Kenny PJ, Cheeta S. The role of dorsal hippocampal serotonergic and cholinergic systems in the modulation of anxiety. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2000;66:65–72. - PubMed
-
- Freidman A, Behrens CJ, Heineman U. Cholinergic dysfunction in temporal lobe epilepsy. Epilepsia. 2007;48:126–30. - PubMed
-
- Wolf NG. Acetylcholine, cognition and consciousness. J Mol Neurosci. 2006;30:219–22. - PubMed
-
- Cummings JL. Cholinesterase inhibitors: a new class of psychotropic compounds. Am J Psychiatry. 2000;157:4–15. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

