Total hip arthroplasty in patients with Down's syndrome
- PMID: 20442995
- PMCID: PMC3080492
- DOI: 10.1007/s00264-010-1030-8
Total hip arthroplasty in patients with Down's syndrome
Abstract
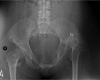
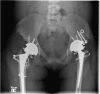
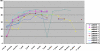
Patients with Down's syndrome (DS) have an increased incidence of coxarthrosis which may become symptomatic with prolonged life expectancy. We present seven consecutive patients (nine hips) with DS who had primary total hip arthroplasty (THA). Average clinical and radiological follow-up was 9.9 ± 6.4 years (range 2-22.25). Harris hip scores (HHS) improved significantly (p < 0.01) from 41.1 (range 18.5-65) to 80.2 (range 67.5-91) at latest follow-up. Two patients required revision arthroplasty for stem loosening at 16 (osteolysis) and six years (trauma) following THA, respectively. Six of the THAs required a constrained liner. No dislocations or deep infections were encountered. We contend that THA is a reliable surgical intervention in patients with DS and may be performed in symptomatic patients.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Total hip arthroplasty in patients with Down syndrome.Orthopedics. 2010 Sep 7;33(9):629. doi: 10.3928/01477447-20100722-32. Orthopedics. 2010. PMID: 20839689
-
Ten-year results after cementless THA with a sandwich-type alumina ceramic bearing.Orthopedics. 2010 Nov 2;33(11):796. doi: 10.3928/01477447-20100924-11. Orthopedics. 2010. PMID: 21053885
-
The 21- to 27-year results of the Harris-Galante cementless total hip arthroplasty.J Orthop Sci. 2016 May;21(3):342-7. doi: 10.1016/j.jos.2016.02.004. Epub 2016 Mar 9. J Orthop Sci. 2016. PMID: 26970833
-
Total Hip Replacements in Patients with Rare Pathologic Conditions Affecting Bone.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2021 Jul 21;103(14):1355-1362. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.20.01398. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2021. PMID: 33780390 Review.
-
Surgical Management of Hip Pain in Active Patients With Early Osteoarthritis: Navigating the Choice Between Hip Preservation and Arthroplasty.J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2025 Apr 1;33(7):336-345. doi: 10.5435/JAAOS-D-24-00242. Epub 2024 Dec 31. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2025. PMID: 39847713 Review.
Cited by
-
Is primary total hip arthroplasty in patients with Down's syndrome associated with increased complications at 2 years follow-up?Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2022 Oct;142(10):2927-2934. doi: 10.1007/s00402-021-04132-3. Epub 2021 Sep 20. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2022. PMID: 34542651
-
Total hip arthroplasty in patients with neuromuscular imbalance.Bone Joint J. 2018 Jan;100-B(1 Supple A):17-21. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.100B1.BJJ-2017-0571.R1. Bone Joint J. 2018. PMID: 29292335 Free PMC article.
-
Management of neck of femur fracture in an adult with short stature and learning disability.BMJ Case Rep. 2022 Feb 10;15(2):e245937. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2021-245937. BMJ Case Rep. 2022. PMID: 35144960 Free PMC article.
-
Hemiarthroplasty for Hip Fracture in Down Syndrome: A Retrospective Series of Five Cases.Hip Pelvis. 2024 Dec 1;36(4):281-289. doi: 10.5371/hp.2024.36.4.281. Hip Pelvis. 2024. PMID: 39620569 Free PMC article.
-
Fresh-stored osteochondral allografts for the treatment of femoral head defects: surgical technique and preliminary results.Int Orthop. 2013 Jun;37(6):1001-6. doi: 10.1007/s00264-013-1868-7. Epub 2013 Apr 4. Int Orthop. 2013. PMID: 23553116 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Stoll C, Alembik Y, Dott B, Roth MP. Study of Down syndrome in 238,942 consecutive births. Ann Genet. 1998;41:44–51. - PubMed
-
- Nance WE, Engel E. Human cytogenetics: a brief review and presentation of new findings. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1967;49:1436–1454. - PubMed
-
- Shaw ED, Beals RK. The hip joint in Down's syndrome. A study of its structure and associated disease. A study of its structure and associated disease. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1992;278:101–107. - PubMed
-
- Penrose LS. The incidence of mongolism in the general population. J Ment Sci. 1949;95:685–688. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

