Simultaneous administration of insulin-like growth factor-1 and darbepoetin alfa protects the rat myocardium against myocardial infarction and enhances angiogenesis
- PMID: 20443814
- PMCID: PMC3016870
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1752-8062.2008.00008.x
Simultaneous administration of insulin-like growth factor-1 and darbepoetin alfa protects the rat myocardium against myocardial infarction and enhances angiogenesis
Abstract
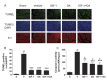
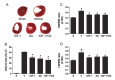
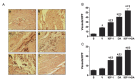
Recent studies have shown that insulin growth factor-1 (IGF-1) and either erythropoietin (EPO) or the long-acting EPO analog Darbepoetin alfa (DA) protect the heart against ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) and myocardial infarction (MI). The present study examined the cardioprotective effect of simultaneous treatments with IGF-1 and DA in these models of cardiac injury. Rats were subjected to I/R or MI and were treated with IGF-1, DA, and a combination of IGF-1 and DA, or vehicle treatment. IGF-1 and DA treatments imparted similar protective effect by reducing infarct size. Moreover, these treatments led to improvement of cardiac function after I/R or MI compared to vehicle. In the reperfused heart, apoptosis was reduced with either or both IGF-1 and DA treatments as measured by reduced TUNEL staining and caspase-3 activity. In addition, after MI, treatment with IGF-1 or DA significantly induced angiogenesis. This angiogenic effect was enhanced significantly when IGF-1 and DA were given simultaneously compared to vehicle or either agents alone. These data indicate simultaneous pharmacological treatments with IGF-1 and DA protect the heart against I/R and MI injuries. This protection results in reduced infarct size and improved cardiac function. Moreover, this treatment reduces apoptosis and enhances angiogenesis in the ischemic heart.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Darbepoetin alfa, a long-acting erythropoietin analog, offers novel and delayed cardioprotection for the ischemic heart.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2007 Jul;293(1):H60-8. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00227.2007. Epub 2007 Mar 23. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17384131
-
Long-term aerobic exercise protects the heart against ischemia/reperfusion injury via PI3 kinase-dependent and Akt-mediated mechanism.Apoptosis. 2007 Sep;12(9):1579-88. doi: 10.1007/s10495-007-0090-8. Apoptosis. 2007. PMID: 17505785
-
Short- and long-term cardioprotective effect of darbepoetin-alpha: role of Bcl-2 family proteins.J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2009 Sep;54(3):223-31. doi: 10.1097/FJC.0b013e3181b04d01. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 19597369
-
Insulin attenuates myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury via reducing oxidative/nitrative stress.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2010 Apr;298(4):E871-80. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00623.2009. Epub 2010 Feb 2. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2010. PMID: 20124508
-
Down-regulation of microRNA-320 suppresses cardiomyocyte apoptosis and protects against myocardial ischemia and reperfusion injury by targeting IGF-1.Oncotarget. 2016 Jun 28;7(26):39740-39757. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.9240. Oncotarget. 2016. Retraction in: Oncotarget. 2025 Mar 13;16:167. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.28704. PMID: 27175593 Free PMC article. Retracted.
Cited by
-
Taohong Siwu Decoction Exerts a Beneficial Effect on Cardiac Function by Possibly Improving the Microenvironment and Decreasing Mitochondrial Fission after Myocardial Infarction.Cardiol Res Pract. 2019 Dec 10;2019:5198278. doi: 10.1155/2019/5198278. eCollection 2019. Cardiol Res Pract. 2019. PMID: 31885903 Free PMC article.
-
Insulin-like growth factor 1 prevents diastolic and systolic dysfunction associated with cardiomyopathy and preserves adrenergic sensitivity.Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2016 Apr;216(4):421-34. doi: 10.1111/apha.12607. Epub 2015 Oct 8. Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2016. PMID: 26399932 Free PMC article.
-
Myocardial injury after ischemia-reperfusion in mice deficient in Akt2 is associated with increased cardiac macrophage density.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2011 Nov;301(5):H1932-40. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00755.2010. Epub 2011 Sep 2. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21890689 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of combination of proliferative agents and erythropoietin on left ventricular remodeling post-myocardial infarction.Clin Transl Sci. 2011 Jun;4(3):168-74. doi: 10.1111/j.1752-8062.2011.00278.x. Clin Transl Sci. 2011. PMID: 21707946 Free PMC article.
-
Myocardial infarction: cardioprotection by erythropoietin.Methods Mol Biol. 2013;982:265-302. doi: 10.1007/978-1-62703-308-4_17. Methods Mol Biol. 2013. PMID: 23456875 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rich MW. Epidemiology, pathophysiology, and etiology of congestive heart failure in older adults. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1994; 45: 968–974. - PubMed
-
- Gross ER, Gross GJ. Ligand triggers of classical preconditioning and postconditioning. Cardiovasc Res. 2006; 70: 212–221. - PubMed
-
- Hausenloy DJ, Yellon DM. New directions for protecting the heart against ischaemia–reperfusion injury: targeting the reperfusion injury salvage kinase (RISK)‐pathway. Cardiovas Res. 2004; 61: 448–460. - PubMed
-
- Constantinescu SN, Ghaffari S, Lodish HF. The erythropoietin receptor: structure, activation and intracellular signal transduction. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 1999; 10: 18–23. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

