The beta1-adrenergic receptor mediates the pharmacogenetic interaction of the ACE D allele and beta-blockers
- PMID: 20443839
- PMCID: PMC5439562
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1752-8062.2008.00020.x
The beta1-adrenergic receptor mediates the pharmacogenetic interaction of the ACE D allele and beta-blockers
Abstract
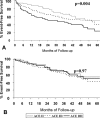
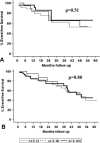
The role of beta-receptor selectivity for the interaction between the angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) insertion/deletion polymorphism and beta-blocker therapy was investigated in 479 subjects with left ventricular dysfunction. Subjects were separated into no beta-blocker, beta1 -selective, and nonselective beta-blocker treatment groups. The D allele adversely affected transplant-free survival for subjects not on beta-blockers (p= 0.004). Treatment with selective beta1-blockers eliminated the impact of the D allele (p= 0.51) in a manner similar to nonselective beta1,2-blockers (p= 0.80). Treatment with beta1-blockers was sufficient to eliminate the adverse impact of the ACE D allele, suggesting this pharmacogenetic interaction is mediated through the beta1-receptor.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pharmacogenetic interactions between beta-blocker therapy and the angiotensin-converting enzyme deletion polymorphism in patients with congestive heart failure.Circulation. 2001 Mar 27;103(12):1644-8. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.103.12.1644. Circulation. 2001. PMID: 11273991 Clinical Trial.
-
Beta-adrenergic receptor blockade and the angiotensin-converting enzyme deletion polymorphism in patients with chronic heart failure.Eur J Heart Fail. 2004 Jan;6(1):17-21. doi: 10.1016/j.ejheart.2003.09.006. Eur J Heart Fail. 2004. PMID: 15012914
-
Pharmacogenomics of heart failure.Methods Mol Biol. 2014;1175:245-57. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-0956-8_10. Methods Mol Biol. 2014. PMID: 25150872
-
Genetic tailoring of pharmacotherapy in heart failure: optimize the old, while we wait for something new.J Card Fail. 2012 Apr;18(4):338-49. doi: 10.1016/j.cardfail.2012.01.002. Epub 2012 Feb 2. J Card Fail. 2012. PMID: 22464776 Review.
-
Angiotensin converting enzyme insertion/deletion polymorphism and renoprotection in diabetic and nondiabetic nephropathies.Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2008 Sep;3(5):1511-25. doi: 10.2215/CJN.04140907. Epub 2008 Jun 11. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2008. PMID: 18550651 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Genomic variation and neurohormonal intervention in heart failure.Heart Fail Clin. 2010 Jan;6(1):35-43. doi: 10.1016/j.hfc.2009.08.004. Heart Fail Clin. 2010. PMID: 19945059 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sigurdsson A, Swedberg K. The role of neurohormonal activation in chronic HF and postmyocardial infarction. Am Heart J. 1996; 132: 229–234. - PubMed
-
- Packer M, Bristow MR, Cohn JN, Colucci WS, Fowler MB, Gilbert EM, Shusterman NH. The effect of carvedilol on morbidity and mortality in patients with chronic heart failure. N Engl J Med. 1996; 334: 1349–1355. - PubMed
-
- Hjalmarson A, Goldstein S, Fagerberg B, Wedel H, Waagstein F, Kjekshus J, Wikstrand J, El Allaf D, Vítovec J, Aldershvile J, Halinen M, Dietz R, Neuhaus KL, Jánosi A, Thorgeirsson G, Dunselman PH, Gullestad L, Kuch J, Herlitz J, Rickenbacher P, Ball S, Gottlieb S, Deedwania P. Effects of controlled‐release metoprolol on total mortality, hospitalizations, and well‐being in patients with heart failure: the Metoprolol CR/XL Randomized Intervention Trial in congestive heart failure (MERIT‐HF). MERIT‐HF study group. JAMA. 2000; 283: 1295–1302. - PubMed
-
- Bristow M. Mechanisms of action of beta‐blocking agents in heart failure. Am J Cardiol. 1997; 80(11A): 26L–40L. - PubMed
-
- Mann DL, Kent RL, Parsons B, Cooper G. Adrenergic effects on the biology of the adult mammalian cardiocyte. Circulation. 1992; 85: 790–804. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

