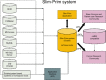
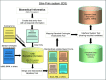
Biomedical Informatics Unit (BMIU): Slim-prim system bridges the gap between laboratory discovery and practice
- PMID: 20443897
- PMCID: PMC5350747
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1752-8062.2009.00109.x
Biomedical Informatics Unit (BMIU): Slim-prim system bridges the gap between laboratory discovery and practice
Abstract
With current national emphasis on translational research, data exchange systems are needed that bridge basic science and clinical research. To meet this challenge, an electronic system was developed by the Biomedical Informatics Unit (BMIU) of the University of Tennessee Clinical Translation Science Institute (UT CTSI). This integrated data system collects, processes, archives, and distributes basic, clinical, and translational research data. The system provides information via web-based applications in a secure and Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA)-compliant manner to facilitate data sharing and analysis across domains. The system is currently in use by a number of studies and has proven to be an effective tool for data collection and processing in clinical studies.
Figures

Comment in
-
Translational medicine lessons from flurizan's failure in Alzheimer's disease (AD) trial: Implication for future drug discovery and development for AD.Clin Transl Sci. 2009 Jun;2(3):242-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1752-8062.2009.00121.x. Clin Transl Sci. 2009. PMID: 20443898 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Slim-prim: a biomedical informatics database to promote translational research.Perspect Health Inf Manag. 2009 May 8;6:6. Perspect Health Inf Manag. 2009. PMID: 19471646 Free PMC article.
-
Addressing the biomedical informatics needs of a microarray laboratory in a clinical microbiology context.Stud Health Technol Inform. 2008;136:45-50. Stud Health Technol Inform. 2008. PMID: 18487706
-
STRIDE--An integrated standards-based translational research informatics platform.AMIA Annu Symp Proc. 2009 Nov 14;2009:391-5. AMIA Annu Symp Proc. 2009. PMID: 20351886 Free PMC article.
-
The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA): its broad effect on practice.Am J Gastroenterol. 2005 Jul;100(7):1440-3. doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2005.50621.x. Am J Gastroenterol. 2005. PMID: 15984962 Review.
-
Temporal reasoning with medical data--a review with emphasis on medical natural language processing.J Biomed Inform. 2007 Apr;40(2):183-202. doi: 10.1016/j.jbi.2006.12.009. Epub 2007 Jan 11. J Biomed Inform. 2007. PMID: 17317332 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Computational framework to support integration of biomolecular and clinical data within a translational approach.BMC Bioinformatics. 2013 Jun 6;14:180. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-14-180. BMC Bioinformatics. 2013. PMID: 23742129 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical data integration of distributed data sources using Health Level Seven (HL7) v3-RIM mapping.J Clin Bioinforma. 2011 Nov 21;1:32. doi: 10.1186/2043-9113-1-32. J Clin Bioinforma. 2011. PMID: 22104558 Free PMC article.
-
Rationale and design of a multicenter randomized clinical trial of extended release gabapentin in provoked vestibulodynia and biological correlates of response.Contemp Clin Trials. 2013 Sep;36(1):154-65. doi: 10.1016/j.cct.2013.06.015. Epub 2013 Jun 29. Contemp Clin Trials. 2013. PMID: 23816491 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

