Translational medicine lessons from flurizan's failure in Alzheimer's disease (AD) trial: Implication for future drug discovery and development for AD
- PMID: 20443898
- PMCID: PMC5350742
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1752-8062.2009.00121.x
Translational medicine lessons from flurizan's failure in Alzheimer's disease (AD) trial: Implication for future drug discovery and development for AD
Figures
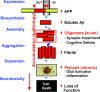
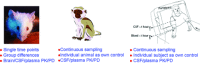
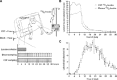
Comment on
-
Biomedical Informatics Unit (BMIU): Slim-prim system bridges the gap between laboratory discovery and practice.Clin Transl Sci. 2009 Jun;2(3):238-41. doi: 10.1111/j.1752-8062.2009.00109.x. Clin Transl Sci. 2009. PMID: 20443897 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Feuerstein GZ. The role of translational medicine and biomarkers research in drug discovery and development. Am Drug Discov. 2007; 2: 23–28.
-
- Feuerstein GZ, Dormer C, Walsh FS, Hurko O, Rutkowski JL. Translational medicine perspectives in drug discovery and development part III: disease biomarkers, disease modifying biomarkers, disease labeling biomarkers and surrogate biomarkers. Am Drug Discov. 2008; 2(4): 36–41.
-
- Feuerstein GZ, Ruffolo RR, Jr , Stiles G, Walsh FS, Rutkowski JL. Translational medicine perspectives of biomarkers in drug discovery and development: part I target selection and validation—biomarkers take center stape. Am Drun Discov. 2007: 2(5): 36–43.
-
- Feuerstein GZ, Dormer C, Ruffolo RR, Jr , Rutkowski JL, Walsh FS, Hurko O. Translational medicine perspectives in drug discovery and development part II: target compound interaction: the vastly neglected biomarkers contributing to early clinical development failure. Am Drug Discov. 2008; 3(2): 48–54.
-
- Selkoe DJ. Alzheimer's disease: genes, proteins, and therapy. Physioi Rev. 2001; 81(2): 741–766. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

