The relationships among immunoglobulin levels, allergic sensitization, and viral respiratory illnesses in early childhood
- PMID: 20444149
- PMCID: PMC3060057
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1399-3038.2010.01041.x
The relationships among immunoglobulin levels, allergic sensitization, and viral respiratory illnesses in early childhood
Abstract
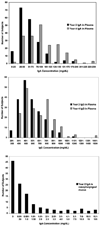
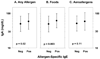
IgE plays an essential role in type I allergy, however, there is less information about the relationship between other immunoglobulins (IgA and IgG) and atopic phenotypes in early childhood. We hypothesized that levels of circulating IgA in early childhood would be inversely related to the number of respiratory infections and the risk of becoming sensitized to allergens. Immunoglobulin levels were analyzed (ELISA) in plasma samples (IgG, IgA), and in nasal secretions (IgA) from children participating in a high-risk birth cohort study. Samples were available from 264 children at age 2 yr and 257 children at age 4 yr, and results were compared to rates of respiratory illnesses, allergic sensitization, atopic dermatitis (AD), and asthma. Children who were sensitized to allergens had higher rather than lower levels of circulating IgA. A subgroup analysis showed that IgA levels were increased in relationship to foods sensitization (58 vs. 50 mg/dl, p = 0.003) but not aeroallergen sensitization (52 vs. 53 mg/dl, p = 0.11). IgA levels in the plasma correlated with levels of IgE levels (r(s) =0.19, p = 0.003). Levels of IgE, but not IgG or IgA, were positively correlated with rates of respiratory illnesses, AD, and the risk of developing asthma. Finally, there were no significant relationships between IgA in nasal secretions and infectious outcomes. In conclusion, low-normal concentrations of plasma IgA are associated with a reduced prevalence of allergic sensitization in infancy. Further, levels of IgA and IgG in plasma within the range of normal, and IgA in nasal secretions, do not appear to influence the risk of subsequent respiratory illnesses. Further studies to define relationships between IgA and allergic sensitization are likely to provide new insights into the pathogenesis of allergic diseases in infancy.
(c) 2010 John Wiley & Sons A/S.
Figures
References
-
- Aghayan-Ugurluoglu R, Ball T, Vrtala S, Schweiger C, Kraft D, Valenta R. Dissociation of allergen-specific IgE and IgA responses in sera and tears of pollen-allergic patients: a study performed with purified recombinant pollen allergens. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2000;105(4):803–813. - PubMed
-
- Ludviksson BR, Eiriksson TH, Ardal B, Sigfusson A, Valdimarsson H. Correlation between serum immunoglobulin A concentrations and allergic manifestations in infants. J Pediatr. 1992;121(1):23–27. - PubMed
-
- Thorarinsdottir HK, Ludviksson BR, Vikingsdottir T, Leopoldsdottir MO, Ardal B, Jonsson T, Valdimarsson H, Arason GJ. Childhood levels of immunoglobulins and mannan-binding lectin in relation to infections and allergy. Scand.J Immunol. 2005;61(5):466–474. - PubMed
-
- Payette K, Weiss NS. Salivary IgA levels in atopic children. Ann Allergy. 1977;39(5):328–331. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

