Carbon monoxide-releasing molecule-2 (CORM-2) attenuates acute hepatic ischemia reperfusion injury in rats
- PMID: 20444253
- PMCID: PMC2873601
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-230X-10-42
Carbon monoxide-releasing molecule-2 (CORM-2) attenuates acute hepatic ischemia reperfusion injury in rats
Abstract
Background: Hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury (I/Ri) is a serious complication occurring during liver surgery that may lead to liver failure. Hepatic I/Ri induces formation of reactive oxygen species, hepatocyte apoptosis, and release of pro-inflammatory cytokines, which together causes liver damage and organ dysfunction. A potential strategy to alleviate hepatic I/Ri is to exploit the potent anti-inflammatory and cytoprotective effects of carbon monoxide (CO) by application of so-called CO-releasing molecules (CORMs). Here, we assessed whether CO released from CORM-2 protects against hepatic I/Ri in a rat model.
Methods: Forty male Wistar rats were randomly assigned into four groups (n = 10). Sham group underwent a sham operation and received saline. I/R group underwent hepatic I/R procedure by partial clamping of portal structures to the left and median lobes with a microvascular clip for 60 minutes, yielding approximately 70% hepatic ischemia and subsequently received saline. CORM-2 group underwent the same procedure and received 8 mg/kg of CORM-2 at time of reperfusion. iCORM-2 group underwent the same procedure and received iCORM-2 (8 mg/kg), which does not release CO. Therapeutic effects of CORM-2 on hepatic I/Ri was assessed by measuring serum damage markers AST and ALT, liver histology score, TUNEL-scoring of apoptotic cells, NFkB-activity in nuclear liver extracts, serum levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines TNF-alpha and IL-6, and hepatic neutrophil infiltration.
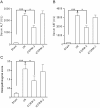
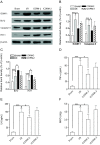
Results: A single systemic infusion with CORM-2 protected the liver from I/Ri as evidenced by a reduction in serum AST/ALT levels and an improved liver histology score. Treatment with CORM-2 also up-regulated expression of the anti-apoptotic protein Bcl-2, down-regulated caspase-3 activation, and significantly reduced the levels of apoptosis after I/Ri. Furthermore, treatment with CORM-2 significantly inhibited the activity of the pro-inflammatory transcription factor NF-kappaB as measured in nuclear extracts of liver homogenates. Moreover, CORM-2 treatment resulted in reduced serum levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines TNF-alpha and IL-6 and down-regulation of the adhesion molecule ICAM-1 in the endothelial cells of liver. In line with these findings, CORM-2 treatment reduced the accumulation of neutrophils in the liver upon I/Ri. Similar treatment with an inactive variant of CORM-2 (iCORM-2) did not have any beneficial effect on the extent of liver I/Ri.
Conclusions: CORM-2 treatment at the time of reperfusion had several distinct beneficial effects on severity of hepatic I/Ri that may be of therapeutic value for the prevention of tissue damage as a result of I/Ri during hepatic surgery.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Effects of carbon monoxide releasing molecule-liberated CO on severe acute pancreatitis in rats.Cytokine. 2010 Jan;49(1):15-23. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2009.09.013. Epub 2009 Nov 8. Cytokine. 2010. PMID: 19900821
-
Systemic application of carbon monoxide-releasing molecule 3 protects skeletal muscle from ischemia-reperfusion injury.J Vasc Surg. 2017 Dec;66(6):1864-1871. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2016.11.065. Epub 2017 Feb 17. J Vasc Surg. 2017. PMID: 28216347
-
Carbon monoxide liberated from CO-releasing molecule (CORM-2) attenuates ischemia/reperfusion (I/R)-induced inflammation in the small intestine.Inflammation. 2010 Apr;33(2):92-100. doi: 10.1007/s10753-009-9162-y. Inflammation. 2010. PMID: 19842024
-
Inflammatory setting, therapeutic strategies targeting some pro-inflammatory cytokines and pathways in mitigating ischemia/reperfusion-induced hepatic injury: a comprehensive review.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2024 Sep;397(9):6299-6315. doi: 10.1007/s00210-024-03074-y. Epub 2024 Apr 21. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38643452 Review.
-
Liver ischemia reperfusion injury: Mechanisms, cellular pathways, and therapeutic approaches.Int Immunopharmacol. 2025 Mar 26;150:114299. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2025.114299. Epub 2025 Feb 16. Int Immunopharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39961215 Review.
Cited by
-
Role of mitofusin 2 in the protective effect of breviscapine against hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats.Exp Ther Med. 2018 Apr;15(4):3582-3588. doi: 10.3892/etm.2018.5834. Epub 2018 Feb 5. Exp Ther Med. 2018. PMID: 29545887 Free PMC article.
-
Hydrophilic CO-Releasing Material of PEGlyated Ruthenium Carbonyl Complex.Materials (Basel). 2022 May 18;15(10):3597. doi: 10.3390/ma15103597. Materials (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35629627 Free PMC article.
-
The Protective Effects of Carbon Monoxide Against Hepatic Warm Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury in MHC-Inbred Miniature Swine.J Gastrointest Surg. 2020 May;24(5):974-982. doi: 10.1007/s11605-019-04283-0. Epub 2019 Jun 26. J Gastrointest Surg. 2020. PMID: 31243716
-
CORM-2-entrapped ultradeformable liposomes ameliorate acute skin inflammation in an ear edema model via effective CO delivery.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2020 Dec;10(12):2362-2373. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2020.05.010. Epub 2020 Jun 10. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2020. PMID: 33354507 Free PMC article.
-
Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor Blockade Reduces Preservation Damage in Livers from Donors after Cardiac Death.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Feb 24;22(5):2234. doi: 10.3390/ijms22052234. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33668105 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lee WY, Lee SM. Ischemic preconditioning protects post-ischemic oxidative damage to mitochondria in rat liver. Shock. 2005;24(4):370–5. doi: 10.1097/01.shk.0000175895.33415.cd. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

