Xenon inhibits excitatory but not inhibitory transmission in rat spinal cord dorsal horn neurons
- PMID: 20444263
- PMCID: PMC2873505
- DOI: 10.1186/1744-8069-6-25
Xenon inhibits excitatory but not inhibitory transmission in rat spinal cord dorsal horn neurons
Abstract
Background: The molecular targets for the promising gaseous anaesthetic xenon are still under investigation. Most studies identify N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptors as the primary molecular target for xenon, but the role of alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazole-4-propionic acid (AMPA) receptors is less clear. In this study we evaluated the effect of xenon on excitatory and inhibitory synaptic transmission in the superficial dorsal horn of the spinal cord using in vitro patch-clamp recordings from rat spinal cord slices. We further evaluated the effects of xenon on innocuous and noxious stimuli using in vivo patch-clamp method.
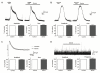
Results: In vitro, xenon decreased the amplitude and area under the curve of currents induced by exogenous NMDA and AMPA and inhibited dorsal root stimulation-evoked excitatory postsynaptic currents. Xenon decreased the amplitude, but not the frequency, of miniature excitatory postsynaptic currents. There was no discernible effect on miniature or evoked inhibitory postsynaptic currents or on the current induced by inhibitory neurotransmitters. In vivo, xenon inhibited responses to tactile and painful stimuli even in the presence of NMDA receptor antagonist.
Conclusions: Xenon inhibits glutamatergic excitatory transmission in the superficial dorsal horn via a postsynaptic mechanism. There is no substantial effect on inhibitory synaptic transmission at the concentration we used. The blunting of excitation in the dorsal horn lamina II neurons could underlie the analgesic effect of xenon.
Figures
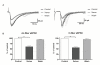



References
-
- Tonner PH, Bangert K, Scholz J. Xenon as a replacement for nitrous oxide? Baillière's Best Practice and Research in Clinical Anaesthesiology. 2001;15:491–503.
-
- Derwall M, Coburn M, Rex S, Hein M, Rossaint R, Fries M. Xenon: recent developments and future perspectives. Minerva Anestesiol. 2009;75:37–45. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

