Effects of phosphodiesterase 4 inhibition on bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in mice
- PMID: 20444277
- PMCID: PMC2881047
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2466-10-26
Effects of phosphodiesterase 4 inhibition on bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in mice
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Effects of phosphodiesterase 4 inhibition on bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in mice.BMC Pulm Med. 2022 Mar 29;22(1):113. doi: 10.1186/s12890-022-01876-5. BMC Pulm Med. 2022. PMID: 35351085 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: Pulmonary fibrosis (PF) is a group of devastating and largely irreversible diseases. Phosphodiesterase (PDE) 4 is involved in the processes of remodeling and inflammation, which play key role in tissue fibrosis. The aim of the study was, therefore, to investigate the effect of PDE4 inhibition in experimental model of PF.
Methods: PF was induced in C57BL/6N mice by instillation of bleomycin. Pharmacological inhibition of PDE4 was achieved by using cilomilast, a selective PDE4 inhibitor. Changes in either lung inflammation or remodeling were evaluated at different stages of experimental PF. Lung inflammation was assessed by bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) differential cell count and reverse transcription quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) for inflammatory cytokines. Changes in tissue remodeling were evaluated by pulmonary compliance measurement, quantified pathological examination, measurement of collagen deposition and RT-qPCR for late remodeling markers. Survival in all groups was analyzed as well.
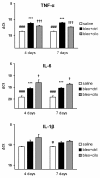
Results: PDE4 inhibition significantly reduced the total number of alveolar inflammatory cells in BALF of mice with bleomycin-induced PF at early fibrosis stage (days 4 and 7). Number of macrophages and lymphocytes, but not neutrophils, was significantly reduced as well. Treatment decreased lung tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha mRNA level and increased mRNA level of interleukin (IL)-6 but did not influence IL-1 beta. At later stage (days 14 and 24) cilomilast improved lung function, which was shown by increase in lung compliance. It also lowered fibrosis degree, as was shown by quantified pathological examination of Hematoxilin-Eosin stained lung sections. Cilomilast had no significant effect on the expression of late remodeling markers such as transforming growth factor (TGF)-beta1 and collagen type Ia1 (COL(I)alpha1). However, it tended to restore the level of lung collagen, assessed by SIRCOL assay and Masson's trichrome staining, and to improve the overall survival.
Conclusions: Selective PDE4 inhibition suppresses early inflammatory stage and attenuates the late stage of experimental pulmonary fibrosis.
Figures




Similar articles
-
[Effects of andrographolide on the concentration of cytokines in BALF and the expressions of type I and III collagen mRNA in lung tissue in bleomycin-induced rat pulmonary fibrosis].Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2011 Jul;27(7):725-9. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2011. PMID: 21722520 Chinese.
-
Zingerone ameliorates oxidative stress and inflammation in bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis: modulation of the expression of TGF-β1 and iNOS.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2020 Sep;393(9):1659-1670. doi: 10.1007/s00210-020-01881-7. Epub 2020 May 6. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32377772
-
Antiflammin-1 attenuates bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in mice.Respir Res. 2013 Oct 8;14(1):101. doi: 10.1186/1465-9921-14-101. Respir Res. 2013. PMID: 24098933 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Advances (2015-2020) in Drug Discovery for Attenuation of Pulmonary Fibrosis and COPD.Molecules. 2023 Apr 24;28(9):3674. doi: 10.3390/molecules28093674. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37175084 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging delivery approaches for targeted pulmonary fibrosis treatment.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2024 Jan;204:115147. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2023.115147. Epub 2023 Dec 6. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2024. PMID: 38065244 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Cytokines in the immunopathology of systemic sclerosis.Semin Immunopathol. 2015 Sep;37(5):543-57. doi: 10.1007/s00281-015-0511-7. Epub 2015 Jul 8. Semin Immunopathol. 2015. PMID: 26152640 Review.
-
Low Gut Microbial Diversity Augments Estrogen-Driven Pulmonary Fibrosis in Female-Predominant Interstitial Lung Disease.Cells. 2023 Feb 28;12(5):766. doi: 10.3390/cells12050766. Cells. 2023. PMID: 36899902 Free PMC article.
-
Beyond epithelial damage: vascular and endothelial contributions to idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.J Clin Invest. 2023 Sep 15;133(18):e172058. doi: 10.1172/JCI172058. J Clin Invest. 2023. PMID: 37712420 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PD-1 up-regulation on CD4+ T cells promotes pulmonary fibrosis through STAT3-mediated IL-17A and TGF-β1 production.Sci Transl Med. 2018 Sep 26;10(460):eaar8356. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aar8356. Sci Transl Med. 2018. PMID: 30257954 Free PMC article.
-
Perspectives of PDE inhibitor on treating idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Feb 14;14:1111393. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1111393. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36865908 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kline JN, Schwartz DA, Monick MM, Floerchinger CS, Hunninghake GW. Relative release of interleukin-1 beta and interleukin-1 receptor antagonist by alveolar macrophages. A study in asbestos-induced lung disease, sarcoidosis, and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Chest. 1993;104:47–53. doi: 10.1378/chest.104.1.47. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Takizawa H, Satoh M, Okazaki H, Matsuzaki G, Suzuki N, Ishii A, Suko M, Okudaira H, Morita Y, Ito K. Increased IL-6 and IL-8 in bronchoalveolar lavage fluids (BALF) from patients with sarcoidosis: correlation with the clinical parameters. Clin Exp Immunol. 1997;107:175–181. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.1997.d01-905.x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

