Hypoxia, HIFs and bone development
- PMID: 20444436
- PMCID: PMC2902564
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bone.2010.04.606
Hypoxia, HIFs and bone development
Abstract
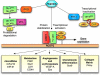
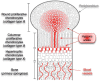
Oxygen is not only an obviously important substrate, but it is also a regulatory signal that controls expression of a specific genetic program. Crucial mediator of the adaptive response of cells to hypoxia is the family of Hypoxia-Inducible Transcription Factors (HIFs).The fetal growth plate, which is an avascular structure of mesenchymal origin, has a unique out-in gradient of oxygenation. HIF-1alpha is necessary for chondrogenesis in vivo by controlling a complex homeostatic response that allows chondrocytes to survive and differentiate in a hypoxic environment. Moreover, HIFs are also essential in osteogenesis and joint development. This brief Perspective summarizes the critical role of HIFs in endochondral bone development.
Copyright 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Posttranslational modifications of collagens as targets of hypoxia and Hif-1alpha in endochondral bone development.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2010 Mar;1192:317-21. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2009.05236.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2010. PMID: 20392253 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Loss of VHL in mesenchymal progenitors of the limb bud alters multiple steps of endochondral bone development.Dev Biol. 2014 Sep 1;393(1):124-36. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2014.06.013. Epub 2014 Jun 24. Dev Biol. 2014. PMID: 24972088 Free PMC article.
-
Fetal growth plate: a developmental model of cellular adaptation to hypoxia.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2007 Nov;1117:26-39. doi: 10.1196/annals.1402.076. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2007. PMID: 18056035 Review.
-
Hypoxia and HIF-1alpha in chondrogenesis.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2006 Apr;1068:66-73. doi: 10.1196/annals.1346.009. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2006. PMID: 16831906 Review.
-
In vivo survival strategies for cellular adaptation to hypoxia: HIF1α-dependent suppression of mitochondrial oxygen consumption and decrease of intracellular hypoxia are critical for survival of hypoxic chondrocytes.Bone. 2020 Nov;140:115572. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2020.115572. Epub 2020 Aug 5. Bone. 2020. PMID: 32768687 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Ultrasonographic Assessment of the Distal Femoral Cartilage Thickness in Patients with Homozygous Sickle Cell Disease.Cartilage. 2016 Jul;7(3):217-21. doi: 10.1177/1947603515614946. Epub 2015 Nov 6. Cartilage. 2016. PMID: 27375836 Free PMC article.
-
Cellular hypoxia promotes osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells and bone defect healing via STAT3 signaling.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2019 Dec 3;24:64. doi: 10.1186/s11658-019-0191-8. eCollection 2019. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2019. PMID: 31827540 Free PMC article.
-
A central role for hypoxic signaling in cartilage, bone, and hematopoiesis.Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2011 Jun;9(2):46-52. doi: 10.1007/s11914-011-0047-2. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2011. PMID: 21360287 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Muscle injury-induced hypoxia alters the proliferation and differentiation potentials of muscle resident stromal cells.Skelet Muscle. 2019 Jun 19;9(1):18. doi: 10.1186/s13395-019-0202-5. Skelet Muscle. 2019. PMID: 31217019 Free PMC article.
-
miRNA-411 Regulates Chondrocyte Autophagy in Osteoarthritis by Targeting Hypoxia-Inducible Factor 1 alpha (HIF-1α).Med Sci Monit. 2020 Feb 19;26:e921155. doi: 10.12659/MSM.921155. Med Sci Monit. 2020. PMID: 32072994 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dunwoodie SL. The role of hypoxia in development of the Mammalian embryo. Dev Cell. 2009;17:755–73. - PubMed
-
- Fryer BH, Simon MC. Hypoxia, HIF and the placenta. Cell Cycle. 2006;5:495–8. - PubMed
-
- Lahiri S, Roy A, Baby SM, Hoshi T, Semenza GL, Prabhakar NR. Oxygen sensing in the body. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2006;91:249–86. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

