Functional cell models of the gut and their applications in food microbiology--a review
- PMID: 20444515
- PMCID: PMC7173225
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2010.03.026
Functional cell models of the gut and their applications in food microbiology--a review
Abstract
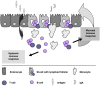
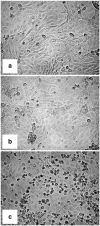
Animal experimentation has a long tradition for risk assessment of new drugs before they reach the clinic. To reduce expensive animal experimentation, attempts have been made to build inexpensive and convenient intestinal functional cell models to study toxicity and bioavailability of new substances along with providing relevant models to study interactions between the host, pathogens and intestinal microflora. We review the available cell lines and models of the intestine and their potential uses. Tumor derived cell lines such as Caco-2, T84 and HT-29 are widely used despite many drawbacks, which are discussed with respect to complexity of the gut, where various cell types interact with commensal microbiota and gut-associated lymphoid tissue. To address this complexity, 3D models of human and animal gut represent a promising in vitro system to mimic in vivo situation without the use of transformed cell lines.
Copyright 2010 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Intestinal in vitro cell culture models and their potential to study the effect of food components on intestinal inflammation.Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2019;59(22):3648-3666. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2018.1506734. Epub 2018 Oct 2. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2019. PMID: 30277794 Review.
-
Evaluating Human Intestinal Cell Lines for Studying Dietary Protein Absorption.Nutrients. 2018 Mar 7;10(3):322. doi: 10.3390/nu10030322. Nutrients. 2018. PMID: 29518965 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Methods to Study Epithelial Transport Protein Function and Expression in Native Intestine and Caco-2 Cells Grown in 3D.J Vis Exp. 2017 Mar 16;(121):55304. doi: 10.3791/55304. J Vis Exp. 2017. PMID: 28362399 Free PMC article.
-
The Roles of Inflammation, Nutrient Availability and the Commensal Microbiota in Enteric Pathogen Infection.Microbiol Spectr. 2015 Jun;3(3). doi: 10.1128/microbiolspec.MBP-0008-2014. Microbiol Spectr. 2015. PMID: 26185088
-
Role of intestinal microflora in xenobiotic-induced toxicity.Mol Nutr Food Res. 2013 Jan;57(1):84-99. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.201200461. Epub 2012 Nov 20. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2013. PMID: 23166009 Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of Lactobacillus spp. on adhesion, invasion, and translocation of Campylobacter jejuni in chicken and pig small-intestinal epithelial cell lines.BMC Vet Res. 2020 Feb 3;16(1):34. doi: 10.1186/s12917-020-2238-5. BMC Vet Res. 2020. PMID: 32013961 Free PMC article.
-
Acute oxidative stress affects IL-8 and TNF-α expression in IPEC-J2 porcine epithelial cells.Inflammation. 2012 Jun;35(3):994-1004. doi: 10.1007/s10753-011-9403-8. Inflammation. 2012. PMID: 22083491
-
Bifidobacteria isolated from infants and cultured on human milk oligosaccharides affect intestinal epithelial function.J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2012 Sep;55(3):321-7. doi: 10.1097/MPG.0b013e31824fb899. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2012. PMID: 22383026 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolites of Lactobacillus plantarum 2142 prevent oxidative stress-induced overexpression of proinflammatory cytokines in IPEC-J2 cell line.Inflammation. 2012 Aug;35(4):1487-99. doi: 10.1007/s10753-012-9462-5. Inflammation. 2012. PMID: 22476971
-
Role of Stress on Driving the Intestinal Paracellular Permeability.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2023 Nov 18;45(11):9284-9305. doi: 10.3390/cimb45110581. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 37998758 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alper J. Glycobiology. Turning sweet on cancer. Science. 2003;301:159–160. - PubMed
-
- Andoh A., Benno Y., Kanauchi O., Fujiyama Y. Recent advances in molecular approaches to gut microbiota in inflammatory bowel disease. Current Pharmaceutical Design. 2009;15:2066–2073. - PubMed
-
- Balimane P.V., Chong S., Morrison R.A. Current methodologies used for evaluation of intestinal permeability and absorption. J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. Methods. 2000;44:301–312. - PubMed
-
- Beaulieu J.F. Extracellular matrix components and integrins in relationship to human intestinal epithelial cell differentiation. Prog. Histochem. Cytochem. 1997;31:1–78. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

