Nonsteroidal selective androgen receptor modulators enhance female sexual motivation
- PMID: 20444881
- PMCID: PMC2913771
- DOI: 10.1124/jpet.110.168880
Nonsteroidal selective androgen receptor modulators enhance female sexual motivation
Abstract
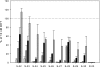
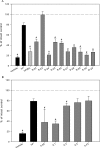
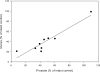
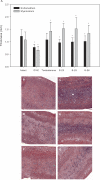
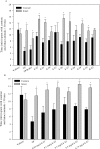
Women experience a decline in estrogen and androgen levels after natural or surgically induced menopause, effects that are associated with a loss of sexual desire and bone mineral density. Studies in our laboratories have shown the beneficial effects of selective androgen receptor modulators (SARMs) in the treatment of osteoporosis and muscle wasting in animal models. A series of S-3-(phenoxy)-2-hydroxy-2-methyl-N-(4-cyano-3-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-propionamide analogs was synthesized to evaluate the effects of B-ring substitutions on in vitro and in vivo pharmacologic activity, especially female sexual motivation. The androgen receptor (AR) relative binding affinities ranged from 0.1 to 26.5% (relative to dihydrotestosterone) and demonstrated a range of agonist activity at 100 nM. In vivo pharmacologic activity was first assessed by using male rats. Structural modifications to the B-ring significantly affected the selectivity of the SARMs, demonstrating that single-atom substitutions can dramatically and unexpectedly influence activity in androgenic (i.e., prostate) and anabolic (i.e., muscle) tissues. (S)-N-(4-cyano-3-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-3-(3-fluoro,4-chlorophenoxy)-2-hydroxy-2-methyl-propanamide (S-23) displayed full agonist activity in androgenic and anabolic tissues; however, the remaining SARMs were more prostate-sparing, selectively maintaining the size of the levator ani muscle in castrated rats. The partner-preference paradigm was used to evaluate the effects of SARMs on female sexual motivation. With the exception of two four-halo substituted analogs, the SARMs increased sexual motivation in ovariectomized rats, with potency and efficacy comparable with testosterone propionate. These results indicate that the AR is important in regulating female libido given the nonaromatizable nature of SARMs and it could be a superior alternative to steroidal testosterone preparations in the treatment of hypoactive sexual desire disorder.
Figures
Comment in
-
Re.: Nonsteroidal selective androgen receptor modulators enhance female sexual motivation.J Urol. 2011 May;185(5):1976-7. doi: 10.1016/S0022-5347(11)60196-1. J Urol. 2011. PMID: 22088744 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Preclinical characterization of a (S)-N-(4-cyano-3-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-3-(3-fluoro, 4-chlorophenoxy)-2-hydroxy-2-methyl-propanamide: a selective androgen receptor modulator for hormonal male contraception.Endocrinology. 2009 Jan;150(1):385-95. doi: 10.1210/en.2008-0674. Epub 2008 Sep 4. Endocrinology. 2009. PMID: 18772237 Free PMC article.
-
A selective androgen receptor modulator for hormonal male contraception.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2005 Feb;312(2):546-53. doi: 10.1124/jpet.104.075424. Epub 2004 Sep 3. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2005. PMID: 15347734
-
Pharmacological characterization of an imidazolopyrazole as novel selective androgen receptor modulator.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2013 Mar;134:51-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2012.10.015. Epub 2012 Oct 23. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2013. PMID: 23098693
-
Androgens and Selective Androgen Receptor Modulators to Treat Functional Limitations Associated With Aging and Chronic Disease.J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2023 Jun 16;78(Suppl 1):25-31. doi: 10.1093/gerona/glad027. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2023. PMID: 37325955 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Selective androgen receptor modulators: in pursuit of tissue-selective androgens.Curr Opin Investig Drugs. 2006 Oct;7(10):873-81. Curr Opin Investig Drugs. 2006. PMID: 17086931 Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of a selective androgen receptor modulator (SARM), GSK2849466A, on stress urinary incontinence and bladder activity in rats with ovariectomy-induced oestrogen deficiency.BJU Int. 2020 Jun;125(6):911-919. doi: 10.1111/bju.15022. Epub 2020 Mar 20. BJU Int. 2020. PMID: 32011085 Free PMC article.
-
Nutrition Optimization Among Critically Ill Patients in the Cardiac Intensive Care Unit.Curr Cardiol Rep. 2025 Apr 4;27(1):79. doi: 10.1007/s11886-025-02208-9. Curr Cardiol Rep. 2025. PMID: 40184002 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Selective Androgen Receptor Modulators: Current Knowledge and Clinical Applications.Sex Med Rev. 2019 Jan;7(1):84-94. doi: 10.1016/j.sxmr.2018.09.006. Epub 2018 Nov 30. Sex Med Rev. 2019. PMID: 30503797 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metabolism-Guided Selective Androgen Receptor Antagonists: Design, Synthesis, and Biological Evaluation for Activity against Enzalutamide-Resistant Prostate Cancer.J Med Chem. 2023 Mar 9;66(5):3372-3392. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.2c01858. Epub 2023 Feb 24. J Med Chem. 2023. PMID: 36825758 Free PMC article.
-
Structural and Functional Evidence for Testosterone Activation of GPRC6A in Peripheral Tissues.Mol Endocrinol. 2015 Dec;29(12):1759-73. doi: 10.1210/me.2015-1161. Epub 2015 Oct 6. Mol Endocrinol. 2015. PMID: 26440882 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abraham GE. (1974) Ovarian and adrenal contribution to peripheral androgens during the menstrual cycle. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 39:340–346 - PubMed
-
- Allan GF, Tannenbaum P, Sbriscia T, Linton O, Lai MT, Haynes-Johnson D, Bhattacharjee S, Zhang X, Sui Z, Lundeen SG. (2007) A selective androgen receptor modulator with minimal prostate hypertrophic activity enhances lean body mass in male rats and stimulates sexual behavior in female rats. Endocrine 32:41–51 - PubMed
-
- Blasberg ME, Robinson S, Henderson LP, Clark AS. (1998) Inhibition of estrogen-induced sexual receptivity by androgens: role of the androgen receptor. Horm Behav 34:283–293 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

