Murine gammaherpesvirus 68 LANA is essential for virus reactivation from splenocytes but not long-term carriage of viral genome
- PMID: 20444892
- PMCID: PMC2898264
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00133-10
Murine gammaherpesvirus 68 LANA is essential for virus reactivation from splenocytes but not long-term carriage of viral genome
Abstract
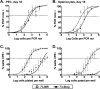
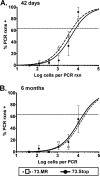
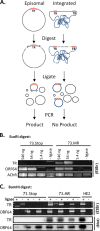
ORF73, which encodes the latency-associated nuclear antigen (LANA), is a conserved gamma-2-herpesvirus gene. The murine gammaherpesvirus 68 (MHV68) LANA (mLANA) is critical for efficient virus replication and the establishment of latent infection following intranasal inoculation. To test whether the initial host immune response limits the capacity of mLANA-null virus to traffic to and establish latency in the spleen, we infected type I interferon receptor knockout (IFN-alpha/betaR(-/-)) mice via intranasal inoculation and observed the presence of viral genome-positive splenocytes at day 18 postinfection at approximately 10-fold-lower levels than in the genetically repaired marker rescue-infected mice. However, no mLANA-null virus reactivation from infected IFN-alpha/betaR(-/-) splenocytes was observed. To more thoroughly define a role of mLANA in MHV68 infection, we evaluated the capacity of an mLANA-null virus to establish and maintain infection apart from restriction in the lungs of immunocompetent mice. At day 18 following intraperitoneal infection of C57BL/6 mice, the mLANA-null virus was able to establish a chronic infection in the spleen albeit at a 5-fold-reduced level. However, as in IFN-alpha/betaR(-/-) mice, little or no virus reactivation could be detected from mLANA-null virus-infected splenocytes upon explant. An examination of peritoneal exudate cells (PECs) following intraperitoneal inoculation revealed nearly equivalent frequencies of PECs harboring the mLANA-null virus relative to the marker rescue virus. Furthermore, although significantly compromised, mLANA-null virus reactivation from PECs was detected upon explant. Notably, at later times postinfection, the frequency of mLANA-null genome-positive splenocytes was indistinguishable from that of marker rescue virus-infected animals. Analyses of viral genome-positive splenocytes revealed the absence of viral episomes in mLANA-null infected mice, suggesting that the viral genome is integrated or maintained in a linear state. Thus, these data provide the first evidence that a LANA homolog is directly involved in the formation and/or maintenance of an extrachromosomal viral episome in vivo, which is likely required for the reactivation of MHV68.
Figures





References
-
- Arbuckle, J. H., M. M. Medveczky, J. Luka, S. H. Hadley, A. Luegmayr, D. Ablashi, T. C. Lund, J. Tolar, K. De Meirleir, J. G. Montoya, A. L. Komaroff, P. F. Ambros, and P. G. Medveczky. 2010. The latent human herpesvirus-6A genome specifically integrates in telomeres of human chromosomes in vivo and in vitro. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 107:5563-5568. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ballestas, M. E., P. A. Chatis, and K. M. Kaye. 1999. Efficient persistence of extrachromosomal KSHV DNA mediated by latency-associated nuclear antigen. Science 284:641-644. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

