Optimal replication of human cytomegalovirus correlates with endocytosis of glycoprotein gpUL132
- PMID: 20444903
- PMCID: PMC2898235
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.01644-09
Optimal replication of human cytomegalovirus correlates with endocytosis of glycoprotein gpUL132
Abstract
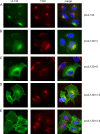
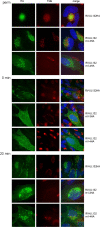
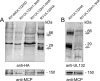
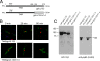
Envelopment of a herpesvirus particle is a complex process of which much is still to be learned. We previously identified the glycoprotein gpUL132 of human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) as an envelope component of the virion. In its carboxy-terminal portion, gpUL132 contains at least four motifs for sorting of transmembrane proteins to endosomes; among them are one dileucine-based signal and three tyrosine-based signals of the YXXØ and NPXY (where X stands for any amino acid, and Ø stands for any bulky hydrophobic amino acid) types. To investigate the role of each of these trafficking signals in intracellular localization and viral replication, we constructed a panel of expression plasmids and recombinant viruses in which the signals were rendered nonfunctional by mutagenesis. In transfected cells wild-type gpUL132 was mainly associated with the trans-Golgi network. Consecutive mutation of the trafficking signals resulted in increasing fractions of the protein localized at the cell surface, with gpUL132 mutated in all four trafficking motifs predominantly associated with the plasma membrane. Concomitant with increased surface expression, endocytosis of mutant gpUL132 was reduced, with a gpUL132 expressing all four motifs in mutated form being almost completely impaired in endocytosis. The replication of recombinant viruses harboring mutations in single trafficking motifs was comparable to replication of wild-type virus. In contrast, viruses containing mutations in three or four of the trafficking signals showed pronounced deficits in replication with a reduction of approximately 100-fold. Moreover, recombinant viruses expressing gpUL132 with three or four trafficking motifs mutated failed to incorporate the mutant protein into the virus particle. These results demonstrate a role of endocytosis of an HCMV envelope glycoprotein for incorporation into the virion and optimal virus replication.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Human Cytomegalovirus Envelope Protein gpUL132 Regulates Infectious Virus Production through Formation of the Viral Assembly Compartment.mBio. 2020 Sep 29;11(5):e02044-20. doi: 10.1128/mBio.02044-20. mBio. 2020. PMID: 32994323 Free PMC article.
-
The cytoplasmic tail of glycoprotein M (gpUL100) expresses trafficking signals required for human cytomegalovirus assembly and replication.J Virol. 2007 Oct;81(19):10316-28. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00375-07. Epub 2007 Jul 11. J Virol. 2007. PMID: 17626081 Free PMC article.
-
Loss of the Human Cytomegalovirus US16 Protein Abrogates Virus Entry into Endothelial and Epithelial Cells by Reducing the Virion Content of the Pentamer.J Virol. 2017 May 12;91(11):e00205-17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00205-17. Print 2017 Jun 1. J Virol. 2017. PMID: 28331097 Free PMC article.
-
The role of virion membrane protein endocytosis in the herpesvirus life cycle.J Clin Virol. 2000 Aug;17(2):69-82. doi: 10.1016/s1386-6532(00)00084-6. J Clin Virol. 2000. PMID: 10942087 Review.
-
Functional roles of short sequence motifs in the endocytosis of membrane receptors.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2009 Jun 1;14(14):5339-60. doi: 10.2741/3599. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2009. PMID: 19482617 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Cytomegaloviruses reorganize endomembrane system to intersect endosomal and amphisome-like egress pathway.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023 Dec 19;11:1328751. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2023.1328751. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023. PMID: 38178873 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Human Cytomegalovirus Hijacks WD Repeat Domain 11 for Virion Assembly Compartment Formation and Virion Morphogenesis.J Virol. 2022 Mar 9;96(5):e0182721. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01827-21. Epub 2022 Jan 12. J Virol. 2022. PMID: 35020472 Free PMC article.
-
Qualitative Differences in Capsidless L-Particles Released as a By-Product of Bovine Herpesvirus 1 and Herpes Simplex Virus 1 Infections.J Virol. 2018 Oct 29;92(22):e01259-18. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01259-18. Print 2018 Nov 15. J Virol. 2018. PMID: 30185590 Free PMC article.
-
Protective capacity of neutralizing and non-neutralizing antibodies against glycoprotein B of cytomegalovirus.PLoS Pathog. 2017 Aug 30;13(8):e1006601. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1006601. eCollection 2017 Aug. PLoS Pathog. 2017. PMID: 28854233 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of Human Cytomegalovirus Secondary Envelopment by a C-Terminal Tetralysine Motif in pUL71.J Virol. 2019 Jun 14;93(13):e02244-18. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02244-18. Print 2019 Jul 1. J Virol. 2019. PMID: 30996102 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alconada, A., U. Bauer, L. Baudoux, J. Piette, and B. Hoflack. 1998. Intracellular transport of the glycoproteins gE and gI of the varicella-zoster virus. gE accelerates the maturation of gI and determines its accumulation in the trans-Golgi network. J. Biol. Chem. 273:13430-13436. - PubMed
-
- Andreoni, M., M. Faircloth, L. Vugler, and W. J. Britt. 1989. A rapid microneutralization assay for the measurement of neutralizing antibody reactive with human cytomegalovirus. J. Virol. Methods 23:157-167. - PubMed
-
- Bi, W., and P. J. Stambrook. 1998. Site-directed mutagenesis by combined chain reaction. Anal. Biochem. 256:137-140. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

