Regulation of (pro)renin receptor expression by glucose-induced mitogen-activated protein kinase, nuclear factor-kappaB, and activator protein-1 signaling pathways
- PMID: 20444941
- PMCID: PMC2903935
- DOI: 10.1210/en.2009-1368
Regulation of (pro)renin receptor expression by glucose-induced mitogen-activated protein kinase, nuclear factor-kappaB, and activator protein-1 signaling pathways
Abstract
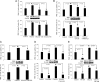
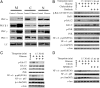
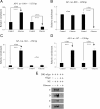
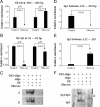
Renal (pro)renin receptor (PRR) expression is increased in diabetes. The exact mechanisms involved in this process are not well established. We hypothesized that high glucose up-regulates PRR through protein kinase C (PKC)-Raf-ERK and PKC-c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK)-c-Jun signaling pathways. Rat mesangial cells exposed to 30 mm d-glucose demonstrated significant increase in PRR mRNA and protein expression, intracellular phosphorylation of Raf-1 (Y340/341), ERK, JNK, nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-kappaB) p65 (S536) and c-Jun (S63). By chromatin immunoprecipitation assay and EMSA, high glucose induced more functional NF-kappaB and activator protein (AP)-1 dimers bound to corresponding cis-regulatory elements in the predicted PRR promoter to up-regulate PRR transcription. Conventional and novel PKC inhibitors Chelerythrine and Rottlerin, Raf-1 inhibitor GW5074, MEK1/2 inhibitor U0126, JNK inhibitor SP600125, NF-kappaB inhibitor Quinazoline, and AP-1 inhibitor Curcumin, respectively, attenuated glucose-induced PRR up-regulation. Chelerythrine and Rottlerin also inhibited glucose-induced phosphorylation of Raf-1 (Y340/341), ERK1/2, JNK, NF-kappaB p65 (S536), and c-Jun (S63). GW5074 and U0126 inhibited the phosphorylation of ERK1/2 and NF-kappaB p65 (S536). SP600125 inhibited phosphorylation of NF-kappaB p65 (S536) and c-Jun (S63). We conclude that high glucose up-regulates the expression of PRR through mechanisms dependent on both PKC-Raf-ERK and PKC-JNK-c-Jun signaling pathways. NF-kappaB and AP-1 are involved in high-glucose-induced PRR up-regulation in rat mesangial cells.
Figures

References
-
- Carey RM, Siragy HM 2003 The intrarenal renin-angiotensin system and diabetic nephropathy. Trends Endocrinol Metab 14:274–281 - PubMed
-
- Carey RM, Siragy HM 2003 Newly recognized components of the renin-angiotensin system: potential roles in cardiovascular and renal regulation. Endocr Rev 24:261–271 - PubMed
-
- Nguyen G, Delarue F, Berrou J, Rondeau E, Sraer JD 1996 Specific receptor binding of renin on human mesangial cells in culture increases plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 antigen. Kidney Int 50:1897–1903 - PubMed
-
- Ludwig J, Kerscher S, Brandt U, Pfeiffer K, Getlawi F, Apps DK, Schägger H 1998 Identification and characterization of a novel 9.2-kDa membrane sector-associated protein of vacuolar proton- ATPase from chromaffin granules. J Biol Chem 273:10939–10947 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

