Interaction of adenosine 3',5'-cyclic monophosphate and tumor necrosis factor-alpha on serum amyloid A3 expression in mouse granulosa cells: dependence on CCAAT-enhancing binding protein-beta isoform
- PMID: 20444945
- PMCID: PMC2903928
- DOI: 10.1210/en.2009-1321
Interaction of adenosine 3',5'-cyclic monophosphate and tumor necrosis factor-alpha on serum amyloid A3 expression in mouse granulosa cells: dependence on CCAAT-enhancing binding protein-beta isoform
Abstract
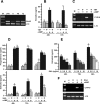
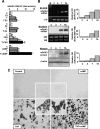
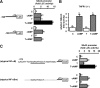
TNFalpha is an inflammatory-related cytokine that has inhibitory effects on gonadotropin- and cAMP-stimulated steroidogenesis and folliculogenesis. Because ovulation is an inflammatory reaction and TNF specifically induces serum amyloid A3 (SAA3) in mouse granulosa cells, the effect of cAMP on TNF-induced SAA3 promoter activity, mRNA and protein was investigated. Granulosa cells from immature mice were cultured with TNF and/or cAMP. TNF increased SAA3 promoter activity, mRNA, and protein, which were further increased by cAMP. cAMP alone increased SAA3 promoter activity, but SAA3 mRNA and protein remained undetectable. Thus, there appeared to be different mechanisms by which TNF and cAMP regulated SAA3 expression. SAA3 promoters lacking a nuclear factor (NF)-kappaB-like site or containing its mutant were not responsive to TNF but were responsive to cAMP. Among four CCAAT-enhancing binding protein (C/EBP) sites in the SAA3 promoter, the C/EBP site nearest the NF-kappaB-like site was required for TNF-induced SAA3. The C/EBP site at -75/-67 was necessary for responsiveness to cAMP. Dominant-negative C/EBP and cAMP response element-binding protein or short interfering RNA of C/EBPbeta blocked TNF- or cAMP-induced SAA3 promoter activity. The combination of TNF and cAMP increased C/EBPbeta protein above that induced by TNF or cAMP alone. Thus, cAMP in combination with TNF specifically induced C/EBPbeta protein, leading to enhanced SAA3 expression but requiring NF-kappaB in mouse granulose cells. In addition, like TNF, SAA inhibited cAMP-induced estradiol accumulation and CYP19 levels. These data indicate SAA may play a role in events occurring during the ovulation process.
Figures


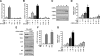
Similar articles
-
Tumor necrosis factor-alpha induces serum amyloid A3 in mouse granulosa cells.Endocrinology. 2004 May;145(5):2245-52. doi: 10.1210/en.2003-1261. Epub 2004 Jan 28. Endocrinology. 2004. PMID: 14749357
-
Regulation of aromatase P450 expression in endometriotic and endometrial stromal cells by CCAAT/enhancer binding proteins (C/EBPs): decreased C/EBPbeta in endometriosis is associated with overexpression of aromatase.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2002 May;87(5):2336-45. doi: 10.1210/jcem.87.5.8486. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2002. PMID: 11994385
-
NF-kappa B and C/EBP transcription factor families synergistically function in mouse serum amyloid A gene expression induced by inflammatory cytokines.Gene. 1994 Nov 18;149(2):305-10. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(94)90166-x. Gene. 1994. PMID: 7959007
-
Induction of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin expression by co-stimulation with interleukin-17 and tumor necrosis factor-alpha is controlled by IkappaB-zeta but neither by C/EBP-beta nor C/EBP-delta.J Biol Chem. 2010 May 7;285(19):14088-100. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.017129. Epub 2010 Mar 10. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20220144 Free PMC article.
-
NFkappa B interacts with serum amyloid A3 enhancer factor to synergistically activate mouse serum amyloid A3 gene transcription.J Biol Chem. 2000 Oct 13;275(41):31616-23. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M005378200. J Biol Chem. 2000. PMID: 10899169
Cited by
-
Localization of Serum Amyloid A3 in the Mouse Ovary.Immune Netw. 2017 Aug;17(4):261-268. doi: 10.4110/in.2017.17.4.261. Epub 2017 Aug 11. Immune Netw. 2017. PMID: 28860955 Free PMC article.
-
CCAAT/enhancer-binding proteins (C/EBP)-α and -β are essential for ovulation, luteinization, and the expression of key target genes.Mol Endocrinol. 2011 Feb;25(2):253-68. doi: 10.1210/me.2010-0318. Epub 2010 Dec 22. Mol Endocrinol. 2011. PMID: 21177758 Free PMC article.
-
Serum Amyloid A3 Secreted by Preosteoclasts Inhibits Parathyroid Hormone-stimulated cAMP Signaling in Murine Osteoblasts.J Biol Chem. 2016 Feb 19;291(8):3882-94. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.686576. Epub 2015 Dec 23. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 26703472 Free PMC article.
-
Augmented Serum Amyloid A1/2 Mediated by TNF-induced NF-κB in Human Serous Ovarian Epithelial Tumors.Immune Netw. 2017 Apr;17(2):121-127. doi: 10.4110/in.2017.17.2.121. Epub 2017 Apr 20. Immune Netw. 2017. PMID: 28458624 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative kinetics of Escherichia coli- and Staphylococcus aureus-specific activation of key immune pathways in mammary epithelial cells demonstrates that S. aureus elicits a delayed response dominated by interleukin-6 (IL-6) but not by IL-1A or tumor necrosis factor alpha.Infect Immun. 2011 Feb;79(2):695-707. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01071-10. Epub 2010 Nov 29. Infect Immun. 2011. PMID: 21115717 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bagavandoss P, Kunkel SL, Wiggins RC, Keyes PL 1988 Tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) production and localization of macrophages and T lymphocytes in the rabbit corpus luteum. Endocrinology 122:1185–1187 - PubMed
-
- Barak V, Mordel N, Holzer H, Zajicek G, Treves AJ, Laufer N 1992 The correlation of interleukin 1 and tumor necrosis factor to oestradiol, progesterone and testosterone levels in periovulatory follicular fluid of in vitro fertilization patients. Hum Reprod 7:462–464 - PubMed
-
- Chen HL, Marcinkiewicz JL, Sancho-Tello M, Hunt JS, Terranova PF 1993 Tumor necrosis factor α gene expression in mouse oocytes and follicular cells. Biol Reprod 48:707–714 - PubMed
-
- Hehnke-Vagnoni KE, Clark CL, Taylor MJ, Ford SP 1995 Presence and localization of tumor necrosis factor-α in the corpus luteum of nonpregnant and pregnant pigs. Biol Reprod 53:1339–1344 - PubMed
-
- Ji I, Slaughter RG, Ellis JA, Ji TH, Murdoch WJ 1991 Analyses of ovine corpora lutea for tumor necrosis factor mRNA and bioactivity during prostaglandin-induced luteolysis. Mol Cell Endocrinol 81:77–80 - PubMed

