Survival of human multiple myeloma cells is dependent on MUC1 C-terminal transmembrane subunit oncoprotein function
- PMID: 20444960
- PMCID: PMC2917857
- DOI: 10.1124/mol.110.065011
Survival of human multiple myeloma cells is dependent on MUC1 C-terminal transmembrane subunit oncoprotein function
Abstract
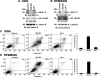
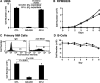
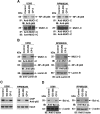
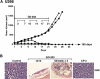
The MUC1 C-terminal transmembrane subunit (MUC1-C) oncoprotein is a direct activator of the canonical nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-kappaB) RelA/p65 pathway and is aberrantly expressed in human multiple myeloma cells. However, it is not known whether multiple myeloma cells are sensitive to the disruption of MUC1-C function for survival. The present studies demonstrate that peptide inhibitors of MUC1-C oligomerization block growth of human multiple myeloma cells in vitro. Inhibition of MUC1-C function also blocked the interaction between MUC1-C and NF-kappaB p65 and activation of the NF-kappaB pathway. In addition, inhibition of MUC1-C in multiple myeloma cells was associated with activation of the intrinsic apoptotic pathway and induction of late apoptosis/necrosis. Primary multiple myeloma cells, but not normal B-cells, were also sensitive to MUC1-C inhibition. Significantly, treatment of established U266 multiple myeloma xenografts growing in nude mice with a lead candidate MUC1-C inhibitor resulted in complete tumor regression and lack of recurrence. These findings indicate that multiple myeloma cells are dependent on intact MUC1-C function for constitutive activation of the canonical NF-kappaB pathway and for their growth and survival.
Figures
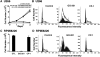
Similar articles
-
MUC1 oncoprotein promotes growth and survival of human multiple myeloma cells.Int J Oncol. 2008 Jul;33(1):153-9. Int J Oncol. 2008. PMID: 18575761 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of the MUC1-C oncoprotein induces multiple myeloma cell death by down-regulating TIGAR expression and depleting NADPH.Blood. 2012 Jan 19;119(3):810-6. doi: 10.1182/blood-2011-07-369686. Epub 2011 Nov 23. Blood. 2012. PMID: 22117045 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting the MUC1-C oncoprotein inhibits self-renewal capacity of breast cancer cells.Oncotarget. 2014 May 15;5(9):2622-34. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.1848. Oncotarget. 2014. PMID: 24770886 Free PMC article.
-
MUC1-C oncoprotein functions as a direct activator of the nuclear factor-kappaB p65 transcription factor.Cancer Res. 2009 Sep 1;69(17):7013-21. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-0523. Epub 2009 Aug 25. Cancer Res. 2009. PMID: 19706766 Free PMC article.
-
MUC1-C oncoprotein as a target in breast cancer: activation of signaling pathways and therapeutic approaches.Oncogene. 2013 Feb 28;32(9):1073-81. doi: 10.1038/onc.2012.158. Epub 2012 May 14. Oncogene. 2013. PMID: 22580612 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting MUC1-C is synergistic with bortezomib in downregulating TIGAR and inducing ROS-mediated myeloma cell death.Blood. 2014 May 8;123(19):2997-3006. doi: 10.1182/blood-2013-11-539395. Epub 2014 Mar 14. Blood. 2014. PMID: 24632713 Free PMC article.
-
MUC1 inhibition leads to decrease in PD-L1 levels via upregulation of miRNAs.Leukemia. 2017 Dec;31(12):2780-2790. doi: 10.1038/leu.2017.163. Epub 2017 May 30. Leukemia. 2017. PMID: 28555079 Free PMC article.
-
Bone marrow stroma protects myeloma cells from cytotoxic damage via induction of the oncoprotein MUC1.Br J Haematol. 2017 Mar;176(6):929-938. doi: 10.1111/bjh.14493. Epub 2017 Jan 20. Br J Haematol. 2017. PMID: 28107546 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and characterization of agonist epitopes of the MUC1-C oncoprotein.Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2014 Feb;63(2):161-74. doi: 10.1007/s00262-013-1494-7. Epub 2013 Nov 15. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2014. PMID: 24233342 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor microenvironment-driven non-cell-autonomous resistance to antineoplastic treatment.Mol Cancer. 2019 Mar 30;18(1):69. doi: 10.1186/s12943-019-0992-4. Mol Cancer. 2019. PMID: 30927928 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Baldus SE, Palmen C, Thiele J. (2007) MUC1 (EMA) expressing plasma cells in bone marrow infiltrated by plasma cell myeloma. Histol Histopathol 22:889–893 - PubMed
-
- Burton J, Mishina D, Cardillo T, Lew K, Rubin A, Goldenberg DM, Gold DV. (1999) Epithelial mucin-1 (MUC1) expression and MA5 anti-MUC1 monoclonal antibody targeting in multiple myeloma. Clin Cancer Res 5 (10 Suppl):3065S–3072S - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

