Bone morphogenetic protein signaling in the developing telencephalon controls formation of the hippocampal dentate gyrus and modifies fear-related behavior
- PMID: 20445055
- PMCID: PMC2905858
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0550-10.2010
Bone morphogenetic protein signaling in the developing telencephalon controls formation of the hippocampal dentate gyrus and modifies fear-related behavior
Abstract
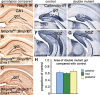
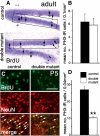
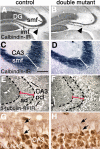
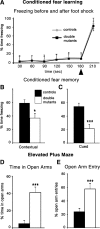
The cortical hem is an embryonic signaling center that generates bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs) and acts as an organizer for the hippocampus. The role of BMP signaling in hippocampal neurogenesis, however, has not been established. We therefore generated mice that were deficient in Bmpr1b constitutively, and deficient in Bmpr1a conditionally in the dorsal telencephalon. In double mutant male and female mice, the dentate gyrus (DG) was dramatically smaller than in control mice, reflecting decreased production of granule neurons at the peak period of DG neurogenesis. Additionally, the pool of cells that generates new DG neurons throughout life was reduced, commensurate with the smaller size of the DG. Effects of diminished BMP signaling on the cortical hem were at least partly responsible for these defects in DG development. Reduction of the DG and its major extrinsic output to CA3 raised the possibility that the DG was functionally compromised. We therefore looked for behavioral deficits in double mutants and found that the mice were less responsive to fear- or anxiety-provoking stimuli, whether the association of the stimulus with fear or anxiety was learned or innate. Given that no anatomical defects appeared in the double mutant telencephalon outside the DG, our observations support a growing literature that implicates the hippocampus in circuitry mediating fear and anxiety. Our results additionally indicate a requirement for BMP signaling in generating the dorsalmost neuronal lineage of the telencephalon, DG granule neurons, and in the development of the stem cell niche that makes neurons in the adult hippocampus.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Bone morphogenic protein signaling is a major determinant of dentate development.J Neurosci. 2013 Apr 17;33(16):6766-75. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0128-13.2013. J Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23595735 Free PMC article.
-
Krüppel-like factor 9 is necessary for late-phase neuronal maturation in the developing dentate gyrus and during adult hippocampal neurogenesis.J Neurosci. 2009 Aug 5;29(31):9875-87. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2260-09.2009. J Neurosci. 2009. PMID: 19657039 Free PMC article.
-
FoxG1 haploinsufficiency results in impaired neurogenesis in the postnatal hippocampus and contextual memory deficits.Hippocampus. 2006;16(10):875-90. doi: 10.1002/hipo.20218. Hippocampus. 2006. PMID: 16941454
-
How to make a hippocampal dentate gyrus granule neuron.Development. 2014 Jun;141(12):2366-75. doi: 10.1242/dev.096776. Development. 2014. PMID: 24917496 Review.
-
[Roles of DISC1-interacting protein Girdin in postnatal development and adult neurogenesis in the dentate gyrus].Nihon Shinkei Seishin Yakurigaku Zasshi. 2011 Feb;31(1):23-8. Nihon Shinkei Seishin Yakurigaku Zasshi. 2011. PMID: 21409841 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
The dynamic role of bone morphogenetic proteins in neural stem cell fate and maturation.Dev Neurobiol. 2012 Jul;72(7):1068-84. doi: 10.1002/dneu.22022. Dev Neurobiol. 2012. PMID: 22489086 Free PMC article. Review.
-
BMP signaling in telencephalic neural cell specification and maturation.Front Cell Neurosci. 2013 Jun 4;7:87. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2013.00087. eCollection 2013. Front Cell Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23761735 Free PMC article.
-
BMP9 protects septal neurons from axotomy-evoked loss of cholinergic phenotype.PLoS One. 2011;6(6):e21166. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0021166. Epub 2011 Jun 13. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21695154 Free PMC article.
-
Growth differentiation factor 5 is a key physiological regulator of dendrite growth during development.Development. 2013 Dec;140(23):4751-62. doi: 10.1242/dev.101378. Epub 2013 Oct 30. Development. 2013. PMID: 24173804 Free PMC article.
-
Whole-genome sequencing of cryopreserved resources from French Large White pigs at two distinct sampling times reveals strong signatures of convergent and divergent selection between the dam and sire lines.Genet Sel Evol. 2023 Mar 2;55(1):13. doi: 10.1186/s12711-023-00789-z. Genet Sel Evol. 2023. PMID: 36864379 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahn K, Mishina Y, Hanks MC, Behringer RR, Crenshaw EB., 3rd BMPR-IA signaling is required for the formation of the apical ectodermal ridge and dorsal-ventral patterning of the limb. Development. 2001;128:4449–4461. - PubMed
-
- Altman J, Bayer SA. Mosaic organization of the hippocampal neuroepithelium and the multiple germinal sources of dentate granule cells. J Comp Neurol. 1990a;301:325–342. - PubMed
-
- Altman J, Bayer SA. Migration and distribution of two populations of hippocampal granule cell precursors during the perinatal and postnatal periods. J Comp Neurol. 1990b;301:365–381. - PubMed
-
- Amaral DG, Witter MP. Hippocampal formation. In: Paxinos G, editor. The rat nervous system. Ed 2. San Diego: Academic; 1995. pp. 443–493.
-
- Andl T, Ahn K, Kairo A, Chu EY, Wine-Lee L, Reddy ST, Croft NJ, Cebra-Thomas JA, Metzger D, Chambon P, Lyons KM, Mishina Y, Seykora JT, Crenshaw EB, 3rd, Millar SE. Epithelial Bmpr1a regulates differentiation and proliferation in postnatal hair follicles and is essential for tooth development. Development. 2004;131:2257–2268. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
