PICK1 regulates incorporation of calcium-permeable AMPA receptors during cortical synaptic strengthening
- PMID: 20445062
- PMCID: PMC2897179
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.6276-09.2010
PICK1 regulates incorporation of calcium-permeable AMPA receptors during cortical synaptic strengthening
Abstract
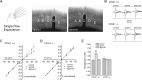
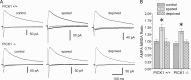
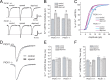
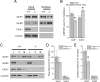
While AMPA-type glutamate receptors (AMPARs) found at principal neuron excitatory synapses typically contain the GluR2 subunit, several forms of behavioral experience have been linked to the de novo synaptic insertion of calcium-permeable (CP) AMPARs, defined by their lack of GluR2. In particular, whisker experience drives synaptic potentiation as well as the incorporation of CP-AMPARs in the neocortex. Previous studies implicate PICK1 (protein interacting with C kinase-1) in activity-dependent internalization of GluR2, suggesting one potential mechanism leading to the subsequent accumulation of synaptic CP-AMPARs and increased synaptic strength. Here we test this hypothesis by using a whisker stimulation paradigm in PICK1 knock-out mice. We demonstrate that PICK1 facilitates the surface expression of CP-AMPARs and is indispensable for their experience-dependent synaptic insertion. However, the failure to incorporate CP-AMPARs in PICK1 knock-outs does not preclude sensory-induced enhancement of synaptic currents. Our results indicate that synaptic strengthening in the early postnatal cortex does not require PICK1 or the addition of GluR2-lacking AMPARs. Instead, PICK1 permits changes in AMPAR subunit composition to occur in conjunction with synaptic potentiation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Developmental expression of Ca2+-permeable AMPA receptors underlies depolarization-induced long-term depression at mossy fiber CA3 pyramid synapses.J Neurosci. 2007 Oct 24;27(43):11651-62. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2671-07.2007. J Neurosci. 2007. PMID: 17959808 Free PMC article.
-
Calcium-permeable AMPA receptor plasticity is mediated by subunit-specific interactions with PICK1 and NSF.Neuron. 2005 Mar 24;45(6):903-15. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2005.02.026. Neuron. 2005. PMID: 15797551
-
PICK1 mediates transient synaptic expression of GluA2-lacking AMPA receptors during glycine-induced AMPA receptor trafficking.J Neurosci. 2012 Aug 22;32(34):11618-30. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5068-11.2012. J Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22915106 Free PMC article.
-
GluA2-lacking, calcium-permeable AMPA receptors--inducers of plasticity?Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2011 Apr;21(2):291-8. doi: 10.1016/j.conb.2011.01.001. Epub 2011 Feb 2. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2011. PMID: 21295464 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of the GluR2 subunit in AMPA receptor function and synaptic plasticity.Neuron. 2007 Jun 21;54(6):859-71. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2007.06.001. Neuron. 2007. PMID: 17582328 Review.
Cited by
-
Role for neonatal D-serine signaling: prevention of physiological and behavioral deficits in adult Pick1 knockout mice.Mol Psychiatry. 2016 Mar;21(3):386-93. doi: 10.1038/mp.2015.61. Epub 2015 May 26. Mol Psychiatry. 2016. PMID: 26008737 Free PMC article.
-
Developmental AMPA receptor subunit specificity during experience-driven synaptic plasticity in the rat barrel cortex.Brain Res. 2012 Jan 30;1435:1-7. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2011.11.033. Epub 2011 Nov 19. Brain Res. 2012. PMID: 22197698 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Findings on AMPA Receptor Recycling.Front Cell Neurosci. 2018 Sep 3;12:286. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2018.00286. eCollection 2018. Front Cell Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30233324 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PICK1 mediates synaptic recruitment of AMPA receptors at neurexin-induced postsynaptic sites.J Neurosci. 2014 Nov 12;34(46):15415-24. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0296-14.2014. J Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 25392508 Free PMC article.
-
Role of phosphoinositides at the neuronal synapse.Subcell Biochem. 2012;59:131-75. doi: 10.1007/978-94-007-3015-1_5. Subcell Biochem. 2012. PMID: 22374090 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bell JD, Park E, Ai J, Baker AJ. PICK1-mediated GluR2 endocytosis contributes to cellular injury after neuronal trauma. Cell Death Differ. 2009;16:1665–1680. - PubMed
-
- Bellone C, Lüscher C. Cocaine triggered AMPA receptor redistribution is reversed in vivo by mGluR-dependent long-term depression. Nat Neurosci. 2006;9:636–641. - PubMed
-
- Benke TA, Lüthi A, Isaac JT, Collingridge GL. Modulation of AMPA receptor unitary conductance by synaptic activity. Nature. 1998;393:793–797. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
