Local control of postinhibitory rebound spiking in CA1 pyramidal neuron dendrites
- PMID: 20445069
- PMCID: PMC3319664
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4066-09.2010
Local control of postinhibitory rebound spiking in CA1 pyramidal neuron dendrites
Abstract
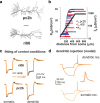
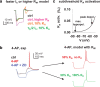
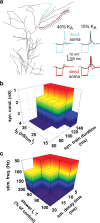
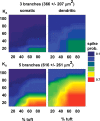
Postinhibitory rebound spiking is characteristic of several neuron types and brain regions, where it sustains spontaneous activity and central pattern generation. However, rebound spikes are rarely observed in the principal cells of the hippocampus under physiological conditions. We report that CA1 pyramidal neurons support rebound spikes mediated by hyperpolarization-activated inward current (I(h)), and normally masked by A-type potassium channels (K(A)). In both experiments and computational models, K(A) blockage or reduction consistently resulted in a somatic action potential upon release from hyperpolarizing injections in the soma or main apical dendrite. Rebound spiking was systematically abolished by the additional blockage or reduction of I(h). Since the density of both K(A) and I(h) increases in these cells with the distance from the soma, such "latent" mechanism may be most effective in the distal dendrites, which are targeted by a variety of GABAergic interneurons. Detailed computer simulations, validated against the experimental data, demonstrate that rebound spiking can result from activation of distal inhibitory synapses. In particular, partial K(A) reduction confined to one or few branches of the apical tuft may be sufficient to elicit a local spike following a train of synaptic inhibition. Moreover, the spatial extent and amount of K(A) reduction determines whether the dendritic spike propagates to the soma. These data suggest that the plastic regulation of K(A) can provide a dynamic switch to unmask postinhibitory spiking in CA1 pyramidal neurons. This newly discovered local modulation of postinhibitory spiking further increases the signal processing power of the CA1 synaptic microcircuitry.
Figures

References
-
- Anderson AE, Adams JP, Qian Y, Cook RG, Pfaffinger PJ, Sweatt JD. Kv4.2 phosphorylation by cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:5337–5346. - PubMed
-
- Armstrong WE, Stern JE. Phenotypic and state-dependent expression of the electrical and morphological properties of oxytocin and vasopressin neurones. Prog Brain Res. 1998;119:101–113. - PubMed
-
- Ascoli GA, Donohue DE, Halavi M. NeuroMorpho.Org: a central resource for neuronal morphologies. J Neurosci. 2007;27:9247–9251. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Balu R, Strowbridge BW. Opposing inward and outward conductances regulate rebound discharges in olfactory mitral cells. J Neurophysiol. 2007;97:1959–1968. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
