Dissolution improvement of electrospun nanofiber-based solid dispersions for acetaminophen
- PMID: 20446072
- PMCID: PMC2902305
- DOI: 10.1208/s12249-010-9438-4
Dissolution improvement of electrospun nanofiber-based solid dispersions for acetaminophen
Abstract
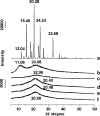
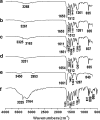
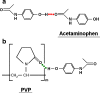
The objective of the present investigation was to prepare novel solid dispersions (SDs) of poorly water-soluble drugs with special microstructural characteristics using electrospinning process. With the hydrophilic polymer polyvinylpyrrolidone as the filament-forming polymer and acetaminophen (APAP) as the poorly water-soluble drug model, SDs having a continuous web structure, and in the form of non-woven nanofiber membranes, were successfully prepared. The electrospun nanofiber-based SDs were compared with those prepared from three traditional SD processes such as freeze-drying, vacuum drying, and heating drying. The surface morphologies, the drug physical status, and the drug-polymer interactions were investigated by scanning electron microscopy, differential scanning calorimetry, X-ray diffraction, and attenuated total reflectance Fourier transform infrared. In vitro dissolution tests demonstrated that the electrospun nanofibers released 93.8% of the APAP content in the first 2 minutes and that the dissolution rates of APAP from the different SDs had the following order: electrospun membrane > vacuum-dried membrane approximately freeze-dried membrane > heat-dried membrane. Electrospun nanofiber-based SDs showed markedly better dissolution-improving effects than the other SDs, mainly due to their huge surface area, high porosity resulting from web structure, and the more homogeneous distribution of APAP in the nanofiber matrix.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

