Phakopsora pachyrhizi, the causal agent of Asian soybean rust
- PMID: 20447267
- PMCID: PMC6640291
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1364-3703.2009.00589.x
Phakopsora pachyrhizi, the causal agent of Asian soybean rust
Abstract
The plant pathogenic basidiomycete fungi Phakopsora pachyrhizi and Phakopsora meibomiae cause rust disease in soybean plants. Phakopsora pachyrhizi originated in Asia-Australia, whereas the less aggressive P. meibomiae originated in Latin America. In the New World, P. pachyrhizi was first reported in the 1990s to have spread to Hawaii and, since 2001, it has been found in South America. In 2004, the pathogen entered continental USA. This review provides detailed information on the taxonomy and molecular biology of the pathogen, and summarizes strategies to combat the threat of this devastating disease.
Taxonomy: Phakopsora pachyrhizi Syd. & P. Syd; uredial anamorph: Malupa sojae (syn. Uredo sojae); Domain Eukaryota; Kingdom Fungi; Phylum Basidiomycota; Order Uredinales; Class Urediniomycetes; Family Phakopsoraceae; Genus Phakopsora (http://www.indexfungorum.org). The nomenclature of rust spores and spore-producing structures used within this review follows Agrios GN (2005) Plant Pathology, 5th edn. London: Elsevier/Academic Press.
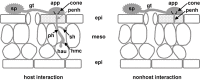
Host range: In the field, P. pachyrhizi infects leaf tissue from a broad range (at least 31 species in 17 genera) of leguminous plants. Infection of an additional 60 species in other genera has been achieved under laboratory conditions.
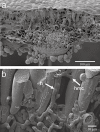
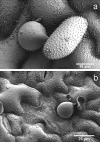
Disease symptoms: At the beginning of the disease, small, tan-coloured lesions, restricted by leaf veins, can be observed on infected soybean leaves. Lesions enlarge and, 5-8 days after initial infection, rust pustules (uredia, syn. uredinia) become visible. Uredia develop more frequently in lesions on the lower surface of the leaf than on the upper surface. The uredia open with a round ostiole through which uredospores are released.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Soybean-Phakopsora pachyrhizi interactions: towards the development of next-generation disease-resistant plants.Plant Biotechnol J. 2024 Feb;22(2):296-315. doi: 10.1111/pbi.14206. Epub 2023 Oct 26. Plant Biotechnol J. 2024. PMID: 37883664 Free PMC article. Review.
-
First Report of Asian Soybean Rust Caused by Phakopsora pachyrhizi in Puerto Rico.Plant Dis. 2013 Oct;97(10):1378. doi: 10.1094/PDIS-01-13-0108-PDN. Plant Dis. 2013. PMID: 30722174
-
First Report of Soybean Rust Caused by Phakopsora pachyrhizi on Phaseolus spp. in the United States.Plant Dis. 2006 Jul;90(7):970. doi: 10.1094/PD-90-0970C. Plant Dis. 2006. PMID: 30781041
-
Effects of Simplicillium lanosoniveum on Phakopsora pachyrhizi, the soybean rust pathogen, and its use as a biological control agent.Phytopathology. 2012 Aug;102(8):749-60. doi: 10.1094/PHYTO-01-11-0031. Phytopathology. 2012. PMID: 22533877
-
From Select Agent to an Established Pathogen: The Response to Phakopsora pachyrhizi (Soybean Rust) in North America.Phytopathology. 2015 Jul;105(7):905-16. doi: 10.1094/PHYTO-02-15-0054-FI. Epub 2015 Jul 1. Phytopathology. 2015. PMID: 25775102 Review.
Cited by
-
New insights into Phakopsora pachyrhizi infection based on transcriptome analysis in planta.Genet Mol Biol. 2018 Jul/Sept.;41(3):671-691. doi: 10.1590/1678-4685-GMB-2017-0161. Genet Mol Biol. 2018. PMID: 30235396 Free PMC article.
-
Soybean-Phakopsora pachyrhizi interactions: towards the development of next-generation disease-resistant plants.Plant Biotechnol J. 2024 Feb;22(2):296-315. doi: 10.1111/pbi.14206. Epub 2023 Oct 26. Plant Biotechnol J. 2024. PMID: 37883664 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genome-wide annotation of the soybean WRKY family and functional characterization of genes involved in response to Phakopsora pachyrhizi infection.BMC Plant Biol. 2014 Sep 10;14:236. doi: 10.1186/s12870-014-0236-0. BMC Plant Biol. 2014. PMID: 25201117 Free PMC article.
-
Interspecies gene transfer provides soybean resistance to a fungal pathogen.Plant Biotechnol J. 2016 Feb;14(2):699-708. doi: 10.1111/pbi.12418. Epub 2015 Jun 10. Plant Biotechnol J. 2016. PMID: 26096357 Free PMC article.
-
Ubiquitous urease affects soybean susceptibility to fungi.Plant Mol Biol. 2012 May;79(1-2):75-87. doi: 10.1007/s11103-012-9894-1. Epub 2012 Mar 1. Plant Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 22382992 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aime, M.C. (2006) Toward resolving family‐level relationships in rust fungi (Uredinales). Mycoscience, 47, 112–122.
-
- Bonde, M.R. (1988) A comparison of isoenzymes of Phakopsora pachyrhizi from the eastern hemisphere and the new world. Phytopathology, 78, 1491–1494.
-
- Bonde, M.R. , Nester, S.E. , Austin, C.N. , Stone, C.L. , Frederick, R.D. , Hartman, G.L. and Miles, M.R. (2006) Evaluation of virulence of Phakopsora pachyrhizi and P. meibomiae isolates. Plant Dis. 90, 708–716. - PubMed
-
- Bromfield, K.R. (1984) Soybean Rust. St. Paul, MN: American Phytopathological Society.
-
- Bromfield, K.R. and Hartwig, E.E. (1980) Resistance to soybean rust and mode of inheritance. Crop. Sci. 20, 254–255.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

