Helper component-proteinase (HC-Pro) protein of Papaya ringspot virus interacts with papaya calreticulin
- PMID: 20447282
- PMCID: PMC6640227
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1364-3703.2009.00606.x
Helper component-proteinase (HC-Pro) protein of Papaya ringspot virus interacts with papaya calreticulin
Abstract
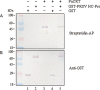
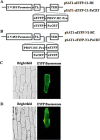
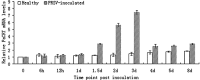
Potyviral helper component-proteinase (HC-Pro) is a multifunctional protein involved in plant-virus interactions. In this study, we constructed a Carica papaya L. plant cDNA library to investigate the host factors interacting with Papaya ringspot virus (PRSV) HC-Pro using a Sos recruitment two-hybrid system (SRS). We confirmed that the full-length papaya calreticulin, designated PaCRT (GenBank accession no. FJ913889), interacts specifically with PRSV HC-Pro in yeast, in vitro and in plant cells using SRS, in vitro protein-binding assay and bimolecular fluorescent complementation assay, respectively. SRS analysis of the interaction between three PaCRT deletion mutants and PRSV HC-Pro demonstrated that the C-domain (residues 307-422), with a high Ca(2+)-binding capacity, was responsible for binding to PRSV HC-Pro. In addition, quantitative real-time reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction assay showed that the expression of PaCRT mRNA was significantly upregulated in the primary stage of PRSV infection, and decreased to near-basal expression levels in noninoculated (healthy) papaya plants with virus accumulation inside host cells. PaCRT is a new calcium-binding protein that interacts with potyviral HC-Pro. It is proposed that the upregulated expression of PaCRT mRNA may be an early defence-related response to PRSV infection in the host plant, and that interaction between PRSV HC-Pro and PaCRT may be involved in plant calcium signalling pathways which could interfere with virus infection or host defence.
Figures




References
-
- Anandalakshmi, R. , Marathe, R. , Ge, X. , Herr, J.M., Jr , Mau, C. , Mallory, A. , Pruss, G. , Bowman, L. and Vance, V.B. (2000) A calmodulin‐related protein that suppresses posttranscriptional gene silencing in plants. Science, 290, 142–144. - PubMed
-
- Ballut, L. , Drucker, M. , Pugnière, M. , Cambon, F. , Blanc, S. , Roquet, F. , Candresse, T. , Schmid, H.P. , Nicolas, P. , Gall, O.L. and Badaoui, S. (2005) HcPro, a multifunctional protein encoded by a plant RNA virus, targets the 20S proteasome and affects its enzymic activities. J. Gen. Virol. 86, 2595–2603. - PubMed
-
- Bau, H.J. , Cheng, Y.H. , Yu, T.A. , Yang, J.S. and Yeh, S.D. (2003) Broad‐spectrum resistance to different geographic strains of papaya ringspot virus in coat protein gene transgenic papaya. Phytopathology 93, 112–120. - PubMed
-
- Bracha‐Drori, K. , Shichrur, K. , Katz, A. , Oliva, M. , Angelovici, R. , Yalovsky, S. and Ohad, N. (2004) Detection of protein–protein interactions in plants using bimolecular fluorescence complementation. Plant J. 40, 419–427. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

