Identification and pre-clinical testing of a reversible cathepsin protease inhibitor reveals anti-tumor efficacy in a pancreatic cancer model
- PMID: 20447439
- PMCID: PMC3814225
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biochi.2010.04.023
Identification and pre-clinical testing of a reversible cathepsin protease inhibitor reveals anti-tumor efficacy in a pancreatic cancer model
Abstract
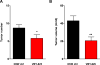
Proteolytic activity is required for several key processes in cancer development and progression, including tumor growth, invasion and metastasis. Accordingly, high levels of protease expression and activity have been found to correlate with malignant progression and poor patient prognosis in a wide variety of human cancers. Members of the papain family of cysteine cathepsins are among the protease classes that have been functionally implicated in cancer. Therefore, the discovery of effective cathepsin inhibitors has considerable potential for anti-cancer therapy. In this study we describe the identification of a novel, reversible cathepsin inhibitor, VBY-825, which has high potency against cathepsins B, L, S and V. VBY-825 was tested in a pre-clinical model of pancreatic islet cancer and found to significantly decrease tumor burden and tumor number. Thus, the identification of VBY-825 as a new and effective anti-tumor drug encourages the therapeutic application of cathepsin inhibitors in cancer.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier Masson SAS. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Rowe RG, Weiss SJ. Navigating ECM barriers at the invasive front: the cancer cell-stroma interface. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2009;25:567–595. - PubMed
-
- Mason SD, Joyce JA. In: Proteolytic cascades in invasion and metastasis, Cancer Metastasis: Biologic Basis and Therapeutics. Welsh DR, Lyden DC, Psaila B, editors. Cambridge University Press; 2010. in press.
-
- Overall CM, Kleifeld O. Tumour microenvironment-opinion: validating matrix metalloproteinases as drug targets and anti-targets for cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 2006;6:227–239. - PubMed
-
- Palermo C, Joyce JA. Cysteine cathepsin proteases as pharmacological targets in cancer. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2008;29:22–28. - PubMed
-
- Ulisse S, Baldini E, Sorrenti S, D'Armiento M. The urokinase plasminogen activator system: a target for anti-cancer therapy. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2009;9:32–71. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

