BDNF increases with behavioral enrichment and an antioxidant diet in the aged dog
- PMID: 20447733
- PMCID: PMC2935515
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2010.03.019
BDNF increases with behavioral enrichment and an antioxidant diet in the aged dog
Abstract
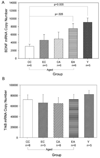
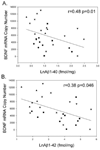
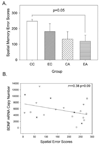
The aged canine (dog) is an excellent model for investigating the neurobiological changes that underlie cognitive impairment and neurodegeneration in humans, as canines and humans undergo similar pathological and behavioral changes with aging. Recent evidence indicates that a combination of environmental enrichment and antioxidant-fortified diet can be used to reduce the rate of age-dependent neuropathology and cognitive decline in aged dogs, although the mechanisms underlying these changes have not been established. We examined the hypothesis that an increase in levels of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) is one of the factors underlying improvements in learning and memory. Old, cognitively impaired animals that did not receive any treatment showed a significant decrease in BDNF mRNA in the temporal cortex when compared with the young group. Animals receiving either an antioxidant diet or environmental enrichment displayed intermediate levels of BDNF mRNA. However, dogs receiving both an antioxidant diet and environmental enrichment showed increased levels of BDNF mRNA when compared with untreated aged dogs, approaching levels measured in young animals. BDNF receptor TrkB mRNA levels did not differ between groups. BDNF mRNA levels were positively correlated with improved cognitive performance and inversely correlated with cortical Aβ((1-42)) and Aβ((1-40)) levels. These findings suggest that environmental enrichment and antioxidant diet interact to maintain brain levels of BDNF, which may lead to improved cognitive performance. This is the first demonstration in a higher animal that nonpharmacological changes in lifestyle in advanced age can upregulate BDNF to levels approaching those in the young brain.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Brain aging in the canine: a diet enriched in antioxidants reduces cognitive dysfunction.Neurobiol Aging. 2002 Sep-Oct;23(5):809-18. doi: 10.1016/s0197-4580(02)00073-8. Neurobiol Aging. 2002. PMID: 12392784 Review.
-
Proteomic identification of brain proteins in the canine model of human aging following a long-term treatment with antioxidants and a program of behavioral enrichment: relevance to Alzheimer's disease.Neurobiol Aging. 2008 Jan;29(1):51-70. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2006.09.012. Epub 2006 Oct 20. Neurobiol Aging. 2008. PMID: 17055614 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of age, dietary, and behavioral enrichment on brain mitochondria in a canine model of human aging.Exp Neurol. 2009 Nov;220(1):171-6. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2009.08.014. Epub 2009 Aug 22. Exp Neurol. 2009. PMID: 19703441 Free PMC article.
-
Synergistic effects of long-term antioxidant diet and behavioral enrichment on beta-amyloid load and non-amyloidogenic processing in aged canines.J Neurosci. 2010 Jul 21;30(29):9831-9. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.6194-09.2010. J Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 20660265 Free PMC article.
-
Combining an antioxidant-fortified diet with behavioral enrichment leads to cognitive improvement and reduced brain pathology in aging canines: strategies for healthy aging.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2007 Oct;1114:398-406. doi: 10.1196/annals.1396.004. Epub 2007 Aug 23. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2007. PMID: 17717087 Review.
Cited by
-
A preclinical cognitive test battery to parallel the National Institute of Health Toolbox in humans: bridging the translational gap.Neurobiol Aging. 2013 Jul;34(7):1891-901. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2013.01.018. Epub 2013 Feb 20. Neurobiol Aging. 2013. PMID: 23434040 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nobiletin Ameliorates the Deficits in Hippocampal BDNF, TrkB, and Synapsin I Induced by Chronic Unpredictable Mild Stress.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013;2013:359682. doi: 10.1155/2013/359682. Epub 2013 Mar 17. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013. PMID: 23573124 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Genistein and Exercise Training on Brain Damage Induced by a High-Fat High-Sucrose Diet in Female C57BL/6 Mice.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022 May 17;2022:1560435. doi: 10.1155/2022/1560435. eCollection 2022. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022. PMID: 35620577 Free PMC article.
-
Changes in mitochondrial function are pivotal in neurodegenerative and psychiatric disorders: how important is BDNF?Br J Pharmacol. 2014 Apr;171(8):2206-29. doi: 10.1111/bph.12531. Br J Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24720259 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The behavioural effect of short-term cognitive and physical intervention therapies in old dogs.Geroscience. 2024 Dec;46(6):5409-5429. doi: 10.1007/s11357-024-01122-2. Epub 2024 Apr 3. Geroscience. 2024. PMID: 38568435 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alderson RF, Alterman AL, Barde YA, Lindsay RM. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor increases survival and differentiated functions of rat septal cholinergic neurons in culture. Neuron. 1990;5(3):297–306. - PubMed
-
- Ando S, Kobayashi S, Waki H, Kon K, Fukui F, Tadenuma T, Iwamoto M, Takeda Y, Izumiyama N, Watanabe K, Nakamura H. Animal model of dementia induced by entorhinal synaptic damage and partial restoration of cognitive deficits by BDNF and carnitine. J Neurosci Res. 2002;70:519–527. - PubMed
-
- Berchtold NC, Chinn G, Chou M, Kesslak JP, Cotman CW. Exercise primes a molecular memory for brain-derived neurotrophic factor protein induction in the rat hippocampus. Neuroscience. 2005;133(3):853–861. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

