Contrast agent kinetics in the rabbit brain during exposure to therapeutic ultrasound
- PMID: 20447757
- PMCID: PMC2878849
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2010.03.005
Contrast agent kinetics in the rabbit brain during exposure to therapeutic ultrasound
Abstract
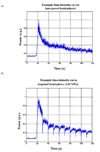
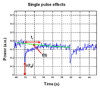
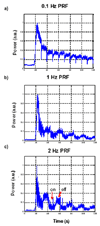
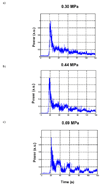
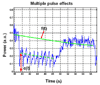
Ultrasound-stimulated microbubbles are currently under investigation as a means of transiently disrupting the blood-brain barrier (BBB) and it has been shown that the strength of this effect is highly dependent on ultrasound exposure conditions. The objective of this study was to investigate the potential for contrast agent destruction in the brain under conditions relevant to BBB disruption with a view to determining its possible influence on effective exposure parameters. An ultrasound imaging array was mounted within the aperture of a 1.68-MHz focused therapy transducer. Pulse lengths of 10 ms were used at repetition rates of 0.1-2.0 Hz and pressures from 0.30-0.88 MPa. Contrast imaging was performed after the bolus injection of Definity, and contrast time-intensity curves were then analyzed for regions-of-interest exposed to the therapy beam. Individual therapy pulses resulted in microbubble destruction, with the degree of agent depletion and replenishment time increasing with transmit pressure. As the pulse repetition rate was increased, agent reperfusion between pulses was incomplete and the concentration within the beam was progressively diminished, to a degree dependent on both pressure and repetition rates. These results demonstrate that microbubble concentration can be substantially influenced by destruction induced by therapeutic ultrasound pulses. The kinetics of this effect may therefore be a significant factor influencing the efficiency of BBB disruption, suggesting that monitoring of the spatial and temporal distribution of contrast agents may be warranted to guide and optimize BBB disruption therapy in both preclinical and clinical contexts.
Copyright 2010 World Federation for Ultrasound in Medicine & Biology. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Blood-brain barrier (BBB) disruption using a diagnostic ultrasound scanner and Definity in Mice.Ultrasound Med Biol. 2009 Aug;35(8):1298-308. doi: 10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2009.03.012. Epub 2009 Jul 9. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2009. PMID: 19545939 Free PMC article.
-
Use of ultrasound pulses combined with Definity for targeted blood-brain barrier disruption: a feasibility study.Ultrasound Med Biol. 2007 Apr;33(4):584-90. doi: 10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2006.10.004. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2007. PMID: 17337109 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of acoustic parameters and ultrasound contrast agent dose on focused-ultrasound induced blood-brain barrier disruption.Ultrasound Med Biol. 2008 Jun;34(6):930-7. doi: 10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2007.11.009. Epub 2008 Feb 21. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2008. PMID: 18294757 Free PMC article.
-
Italian Society of Cardiovascular Echography (SIEC) Consensus Conference on the state of the art of contrast echocardiography.Ital Heart J. 2004 Apr;5(4):309-34. Ital Heart J. 2004. PMID: 15185894 Review.
-
Ultrasound, microbubbles and the blood-brain barrier.Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2007 Jan-Apr;93(1-3):354-62. doi: 10.1016/j.pbiomolbio.2006.07.019. Epub 2006 Aug 4. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2007. PMID: 16959303 Review.
Cited by
-
An experimental study on the stiffness of size-isolated microbubbles using atomic force microscopy.IEEE Trans Ultrason Ferroelectr Freq Control. 2013 Mar;60(3):524-34. doi: 10.1109/TUFFC.2013.2594. IEEE Trans Ultrason Ferroelectr Freq Control. 2013. PMID: 23475918 Free PMC article.
-
Ultrasound-Propelled Nanocups for Drug Delivery.Small. 2015 Oct 21;11(39):5305-14. doi: 10.1002/smll.201501322. Epub 2015 Aug 21. Small. 2015. PMID: 26296985 Free PMC article.
-
Image-guided ultrasound phased arrays are a disruptive technology for non-invasive therapy.Phys Med Biol. 2016 Sep 7;61(17):R206-48. doi: 10.1088/0031-9155/61/17/R206. Epub 2016 Aug 5. Phys Med Biol. 2016. PMID: 27494561 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Two-photon fluorescence microscopy study of cerebrovascular dynamics in ultrasound-induced blood-brain barrier opening.J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2011 Sep;31(9):1852-62. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.2011.59. Epub 2011 Apr 20. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2011. PMID: 21505473 Free PMC article.
-
Contrast-enhanced ultrasound imaging for the detection of focused ultrasound-induced blood-brain barrier opening.Theranostics. 2014 Aug 1;4(10):1014-25. doi: 10.7150/thno.9575. eCollection 2014. Theranostics. 2014. PMID: 25161701 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arditi M, Frinking PJA, Zhou X, Rognin NG. A new formalism for the quantification of tissue perfusion by the destruct ion-replenishment method in contrast ultrasound imaging. IEEE Trans Ultrasonics Ferroelect Freq Contr. 2006;53:1118–1129. - PubMed
-
- Choi JJ, Pernot M, Small SA, Konofagou EE. Noninvasive, transcranial and localized opening of the blood-brain barrier using focused ultrasound in mice. Phys Med Biol. 2007;52:5509–5530. - PubMed
-
- Chomas JE, Dayton P, Allen J, Ferrara KW. Mechanisms of contrast agent destruction. IEEE Ultrason Ferroelec Freq Control. 2001;48:232–248. - PubMed
-
- Clement GT, White J, Hynynen K. Investigation of a large-area phased array for focused ultrasound surgery through the skull. Phys Med Biol. 2000;45:1071–1083. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

