Rituximab (Rituxan)
- PMID: 20448016
- PMCID: PMC7965451
- DOI: 10.3174/ajnr.A2142
Rituximab (Rituxan)
Abstract
Rituximab is a monoclonal antibody that was first approved by the FDA as an antineoplastic agent designed to treat B-cell malignancies. This article will review the mechanism of action and clinical role of this anti-B-cell agent.
Figures
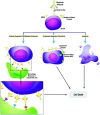
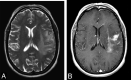
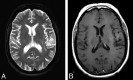
References
-
- McLaughlin P, Grillo-Lopez AJ, Link BK, et al. Rituximab chimeric anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody therapy for relapsed indolent lymphoma: half of patients respond to a four dose treatment program. J Clin Oncol 1998;16:2825–33 - PubMed
-
- Marcus R, Imrie K, Belch A, et al. CVP chemotherapy plus rituximab compared with CVP as first-line treatment for advanced follicular lymphoma. Blood 2005;105:1417–23. Epub 2004 Oct 19 - PubMed
-
- Coiffier B, Lepage E, Briere J, et al. CHOP chemotherapy plus rituximab compared with CHOP alone in elderly patients with diffuse large-B-cell lymphoma. N Engl J Med 2002;346:235–42 - PubMed
-
- Edwards JC, Szczepanski L, Szechinski J, et al. Efficacy of B-cell-targeted therapy with rituximab in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med 2004;350:2572–81 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
