Regulation of the nitrogen transfer pathway in the arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis: gene characterization and the coordination of expression with nitrogen flux
- PMID: 20448102
- PMCID: PMC2899933
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.110.156430
Regulation of the nitrogen transfer pathway in the arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis: gene characterization and the coordination of expression with nitrogen flux
Abstract
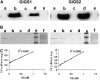
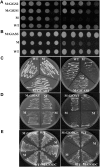
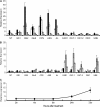
The arbuscular mycorrhiza (AM) brings together the roots of over 80% of land plant species and fungi of the phylum Glomeromycota and greatly benefits plants through improved uptake of mineral nutrients. AM fungi can take up both nitrate and ammonium from the soil and transfer nitrogen (N) to host roots in nutritionally substantial quantities. The current model of N handling in the AM symbiosis includes the synthesis of arginine in the extraradical mycelium and the transfer of arginine to the intraradical mycelium, where it is broken down to release N for transfer to the host plant. To understand the mechanisms and regulation of N transfer from the fungus to the plant, 11 fungal genes putatively involved in the pathway were identified from Glomus intraradices, and for six of them the full-length coding sequence was functionally characterized by yeast complementation. Two glutamine synthetase isoforms were found to have different substrate affinities and expression patterns, suggesting different roles in N assimilation. The spatial and temporal expression of plant and fungal N metabolism genes were followed after nitrate was added to the extraradical mycelium under N-limited growth conditions using hairy root cultures. In parallel experiments with (15)N, the levels and labeling of free amino acids were measured to follow transport and metabolism. The gene expression pattern and profiling of metabolites involved in the N pathway support the idea that the rapid uptake, translocation, and transfer of N by the fungus successively trigger metabolic gene expression responses in the extraradical mycelium, intraradical mycelium, and host plant.
Figures
References
-
- Ames RN, Reid CP, Porter LK, Cambardella C. (1983) Hyphal uptake and transport of nitrogen from two 15N-labelled sources by Glomus mosseae, a vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus. New Phytol 95: 381–396
-
- Bagni N, Malucelli B, Torrigiani P. (1980) Polyamines, storage substances and abscisic acid-like inhibitors during dormancy and very early activation of Helianthus tuberosus tuber tissues. Physiol Plant 49: 341–345
-
- Bago B, Pfeffer P, Shachar-Hill Y. (2001) Could the urea cycle be translocating nitrogen in the arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis? New Phytol 149: 4–8 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

