Synergistic growth inhibition of anaplastic large cell lymphoma cells by combining cellular ALK gene silencing and a low dose of the kinase inhibitor U0126
- PMID: 20448669
- PMCID: PMC2919633
- DOI: 10.1038/cgt.2010.20
Synergistic growth inhibition of anaplastic large cell lymphoma cells by combining cellular ALK gene silencing and a low dose of the kinase inhibitor U0126
Abstract
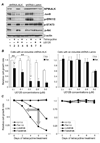
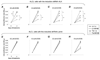
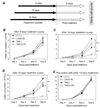
Abnormal expression of anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) gene is an important pathogenic factor for anaplastic large cell lymphoma (ALCL). To study the function of ALK, an inducible short hairpin RNA (shRNA) system was stably introduced into cultured human ALCL cells. Inducing shRNA expression in the generated cells resulted in cellular ALK gene silencing and led to inactivation of multiple signaling pathways and growth arrest. Interestingly, a combination of ALK gene silencing with U0126, a kinase inhibitor specific for the extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1/2 pathway, resulted in an augmented reduction in cellular JunB expression. Functional studies indicated that combining ALK gene silencing with U0126 treatment provided a synergistic growth inhibition, which occurred faster and was more profound than with either treatment alone. This synergistic effect was also observed when measuring cell proliferation, apoptosis, and in vitro cell colony formation. Importantly, the combination of ALK gene silencing and U0126 had a prolonged inhibitory effect, preventing recovery of ALCL cell growth even after treatments were removed. Moreover, this synergistic inhibitory effect was confirmed in vivo using a mouse model with xenografted ALCL tumors. Our findings indicate that combining cellular ALK gene silencing with a low dose of U0126 may prove to be an effective and more specific therapeutic approach to treating ALCL.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




Similar articles
-
The HSP90 inhibitor 17-AAG synergizes with doxorubicin and U0126 in anaplastic large cell lymphoma irrespective of ALK expression.Exp Hematol. 2006 Dec;34(12):1670-9. doi: 10.1016/j.exphem.2006.07.002. Exp Hematol. 2006. PMID: 17157164
-
STAT1 is phosphorylated and downregulated by the oncogenic tyrosine kinase NPM-ALK in ALK-positive anaplastic large-cell lymphoma.Blood. 2015 Jul 16;126(3):336-45. doi: 10.1182/blood-2014-10-603738. Epub 2015 Apr 28. Blood. 2015. PMID: 25921060
-
Therapeutic efficacy of the bromodomain inhibitor OTX015/MK-8628 in ALK-positive anaplastic large cell lymphoma: an alternative modality to overcome resistant phenotypes.Oncotarget. 2016 Nov 29;7(48):79637-79653. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.12876. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27793034 Free PMC article.
-
Nucleophosmin-anaplastic lymphoma kinase: the ultimate oncogene and therapeutic target.Blood. 2017 Feb 16;129(7):823-831. doi: 10.1182/blood-2016-05-717793. Epub 2016 Nov 22. Blood. 2017. PMID: 27879258 Review.
-
Molecular biology of anaplastic lymphoma kinase-positive anaplastic large-cell lymphoma.J Clin Oncol. 2002 Sep 1;20(17):3691-702. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2002.12.033. J Clin Oncol. 2002. PMID: 12202671 Review.
Cited by
-
Aristolochic acid I induced autophagy extenuates cell apoptosis via ERK 1/2 pathway in renal tubular epithelial cells.PLoS One. 2012;7(1):e30312. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0030312. Epub 2012 Jan 20. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22276178 Free PMC article.
-
pH-responsive DNA nanomicelles for chemo-gene synergetic therapy of anaplastic large cell lymphoma.Theranostics. 2020 Jul 9;10(18):8250-8263. doi: 10.7150/thno.45803. eCollection 2020. Theranostics. 2020. PMID: 32724469 Free PMC article.
-
Transfection of shRNA-encoding Minivector DNA of a few hundred base pairs to regulate gene expression in lymphoma cells.Gene Ther. 2011 Mar;18(3):220-4. doi: 10.1038/gt.2010.123. Epub 2010 Oct 21. Gene Ther. 2011. PMID: 20962872 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery of a new method for potent drug development using power function of stoichiometry of homomeric biocomplexes or biological nanomotors.Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2016;13(1):23-36. doi: 10.1517/17425247.2015.1082544. Epub 2015 Aug 24. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2016. PMID: 26307193 Free PMC article.
-
PI3K-AKT-mTOR-signaling and beyond: the complex network in gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasms.Theranostics. 2014 Jan 29;4(4):336-65. doi: 10.7150/thno.7851. eCollection 2014. Theranostics. 2014. PMID: 24578720 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Adjei AA, Cohen RB, Franklin W, Morris C, Wilson D, Molina JR, et al. Phase I pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic study of the oral, small-molecule mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 1/2 inhibitor AZD6244 (ARRY-142886) in patients with advanced cancers. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26:2139–2146. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bai RY, Ouyang T, Miething C, Morris SW, Peschel C, Duyster J. Nucleophosmin-anaplastic lymphoma kinase associated with anaplastic large-cell lymphoma activates the phosphatidylinositol phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt antiapoptotic signaling pathway. Blood. 2000;96:4319–4327. - PubMed
-
- Chiarle R, Gong JZ, Guasparri I, Pesci A, Cai J, Liu J, et al. NPM-ALK transgenic mice spontaneously develop T-cell lymphomas and plasma cell tumors. Blood. 2003;101:1919–1927. - PubMed
-
- Chiarle R, Simmons WJ, Cai H, Dhall G, Zamo A, Raz R, et al. Stat3 is required for ALK-mediated lymphomagenesis and provides a possible therapeutic target. Nat Med. 2005;11:623–629. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

