Inteins, valuable genetic elements in molecular biology and biotechnology
- PMID: 20449740
- PMCID: PMC2874743
- DOI: 10.1007/s00253-010-2628-x
Inteins, valuable genetic elements in molecular biology and biotechnology
Abstract
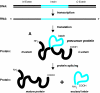
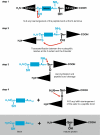
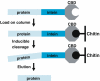
Inteins are internal protein elements that self-excise from their host protein and catalyze ligation of the flanking sequences (exteins) with a peptide bond. They are found in organisms in all three domains of life, and in viral proteins. Intein excision is a posttranslational process that does not require auxiliary enzymes or cofactors. This self-excision process is called protein splicing, by analogy to the splicing of RNA introns from pre-mRNA. Protein splicing involves only four intramolecular reactions, and a small number of key catalytic residues in the intein and exteins. Protein-splicing can also occur in trans. In this case, the intein is separated into N- and C-terminal domains, which are synthesized as separate components, each joined to an extein. The intein domains reassemble and link the joined exteins into a single functional protein. Understanding the cis- and trans-protein splicing mechanisms led to the development of intein-mediated protein-engineering applications, such as protein purification, ligation, cyclization, and selenoprotein production. This review summarizes the catalytic activities and structures of inteins, and focuses on the advantages of some recent intein applications in molecular biology and biotechnology.
Figures
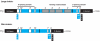

References
-
- Arnér ES, Sarioglu H, Lottspeich F, Holmgren A, Bock A. High-level expression in Escherichia coli of selenocysteine-containing rat thioredoxin reductase utilizing gene fusions with engineered bacterial-type SECIS elements and co-expression with the selA, selB and selC genes. J Mol Biol. 1999;292:1003–1016. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1999.3085. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Arnér ES, Cheng Q, Donald HJ. Method for producing selenoproteins. United Nations: World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO); 2009.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

