Comparative transcriptomics and proteomics of p-hydroxybenzoate producing Pseudomonas putida S12: novel responses and implications for strain improvement
- PMID: 20449741
- PMCID: PMC2874742
- DOI: 10.1007/s00253-010-2626-z
Comparative transcriptomics and proteomics of p-hydroxybenzoate producing Pseudomonas putida S12: novel responses and implications for strain improvement
Abstract
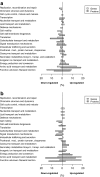
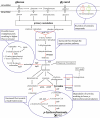
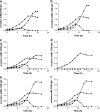
A transcriptomics and proteomics approach was employed to study the expression changes associated with p-hydroxybenzoate production by the engineered Pseudomonas putida strain S12palB1. To establish p-hydroxybenzoate production, phenylalanine-tyrosine ammonia lyase (pal/tal) was introduced to connect the tyrosine biosynthetic and p-coumarate degradation pathways. In agreement with the efficient p-hydroxybenzoate production, the tyrosine biosynthetic and p-coumarate catabolic pathways were upregulated. Also many transporters were differentially expressed, one of which--a previously uncharacterized multidrug efflux transporter with locus tags PP1271-PP1273--was found to be associated with p-hydroxybenzoate export. In addition to tyrosine biosynthesis, also tyrosine degradative pathways were upregulated. Eliminating the most prominent of these resulted in a 22% p-hydroxybenzoate yield improvement. Remarkably, the upregulation of genes contributing to p-hydroxybenzoate formation was much higher in glucose than in glycerol-cultured cells.
Figures

References
-
- Ballerstedt H, Volkers RJM, Mars AE, Hallsworth JE, Santos VA, Puchalka J, van Duuren J, Eggink G, Timmis KN, de Bont JAM, Wery J. Genomotyping of Pseudomonas putida strains using P. putida KT2440-based high-density DNA microarrays: implications for transcriptomics studies. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2007;75:1133–1142. doi: 10.1007/s00253-007-0914-z. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

