Factors associated with mortality in transplant patients with invasive aspergillosis
- PMID: 20450350
- PMCID: PMC2874071
- DOI: 10.1086/652768
Factors associated with mortality in transplant patients with invasive aspergillosis
Abstract
Background: Invasive aspergillosis (IA) is an important cause of morbidity and mortality in hematopoietic stem cell transplant (HSCT) and solid organ transplant (SOT) recipients. The purpose of this study was to evaluate factors associated with mortality in transplant patients with IA.
Methods: Transplant patients from 23 US centers were enrolled from March 2001 to October 2005 as part of the Transplant Associated Infection Surveillance Network. IA cases were identified prospectively in this cohort through March 2006, and data were collected. Factors associated with 12-week all-cause mortality were determined by logistic regression analysis and Cox proportional hazards regression.
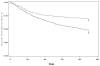
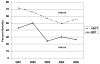
Results: Six-hundred forty-two cases of proven or probable IA were evaluated, of which 317 (49.4%) died by the study endpoint. All-cause mortality was greater in HSCT patients (239 [57.5%] of 415) than in SOT patients (78 [34.4%] of 227; P<.001). Independent poor prognostic factors in HSCT patients were neutropenia, renal insufficiency, hepatic insufficiency, early-onset IA, proven IA, and methylprednisolone use. In contrast, white race was associated with decreased risk of death. Among SOT patients, hepatic insufficiency, malnutrition, and central nervous system disease were poor prognostic indicators, whereas prednisone use was associated with decreased risk of death. Among HSCT or SOT patients who received antifungal therapy, use of an amphotericin B preparation as part of initial therapy was associated with increased risk of death.
Conclusions: There are multiple variables associated with survival in transplant patients with IA. Understanding these prognostic factors may assist in the development of treatment algorithms and clinical trials.
Figures
References
-
- Parody R, Martino R, Sanchez F, et al. Predicting survival in adults with invasive aspergillosis during therapy for hematological malignancies or after hematopoietic stem cell transplanation : Single-center analysis and validation of the Seattle, French, and Strasbourg prognostic indexes. Am J Hematol. 2009;84(9):571–8. - PubMed
-
- Marr KA, Carter RA, Crippa F, Wald A, Corey L. Epidemiology and outcome of mould infections in hematopoietic stem cell transplant recipients. Clin Infect Dis. 2002;34(7):909–17. - PubMed
-
- Cordonnier C, Ribaud P, Herbrecht R, et al. Prognostic factors for death due to invasive aspergillosis after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: a 1-year retrospective study of consecutive patients at French transplantation centers. Clin Infect Dis. 2006;42(7):955–63. - PubMed
-
- Upton A, Kirby KA, Carpenter P, Boeckh M, Marr KA. Invasive aspergillosis following hematopoietic cell transplantation: outcomes and prognostic factors associated with mortality. Clin Infect Dis. 2007;44(4):531–40. - PubMed
-
- Ribaud P, Chastang C, Latge JP, et al. Survival and prognostic factors of invasive aspergillosis after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. Clin Infect Dis. 1999;28(2):322–30. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

