Reversed shoulder arthroplasty in cuff tear arthritis, fracture sequelae, and revision arthroplasty
- PMID: 20450427
- PMCID: PMC2876841
- DOI: 10.3109/17453674.2010.487242
Reversed shoulder arthroplasty in cuff tear arthritis, fracture sequelae, and revision arthroplasty
Abstract
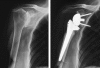
Background and purpose: Reversed shoulder arthroplasty may be used for severe arthropathy where conventional prostheses cannot restore the function sufficiently. We analyzed the medium-term results and potential complications of the reversed prostheses, and also the influence of etiology on the result. METHODS; 52 women and 7 men, average age 70 (60-82) years, were followed for mean 4 (2-7) years. The indications were cuff tear arthropathy (CTA) (23), fracture sequelae (20), and revision of a failed conventional arthroplasty (16).
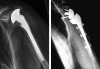
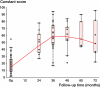
Results: The average Constant score improved from 18 (2-55) points to 59 (17-96) points. It rose from 26 to 74 points in patients with CTA, from 12 to 48 in those with fracture sequelae, and from 10 to 54 points in revision arthroplasty. We also found an overall improvement in active forward flexion from 47 degrees to 105 degrees , and in active abduction from 46 degrees to 93 degrees . Scapular notching was seen in 51 shoulders. Radiolucent lines below the base-plate were present in 2 cases. There were no instances of loosening. Revisions were necessary in 15 patients: 5 with infections (all had had prior surgery), 5 with hematoma, 3 with dislocations, and 2 with disconnections of the shaft components.
Interpretation: Reversed prosthetic replacement is a suitable method for restoring function and attaining pain relief in severe arthropathies. The results in revision arthroplasty are less predictable, with complications and revision rates higher than those in CTA patients. The reversed prosthesis should therefore only be used when conventional methods have failed.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Neer Award 2005: The Grammont reverse shoulder prosthesis: results in cuff tear arthritis, fracture sequelae, and revision arthroplasty.J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2006 Sep-Oct;15(5):527-40. doi: 10.1016/j.jse.2006.01.003. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2006. PMID: 16979046
-
Reverse total shoulder arthroplasty: a review of results according to etiology.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007 Jul;89(7):1476-85. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.F.00666. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007. PMID: 17606786
-
Short and midterm results of reverse shoulder arthroplasty according to the preoperative etiology.Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2013 Apr;133(4):463-71. doi: 10.1007/s00402-013-1688-7. Epub 2013 Feb 6. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2013. PMID: 23385301
-
Use of the reverse shoulder prosthesis for the treatment of failed hemiarthroplasty in patients with glenohumeral arthritis and rotator cuff deficiency.J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2007 Feb;89(2):189-95. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.89B2.18161. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2007. PMID: 17322433 Review.
-
Revision of failed total shoulder arthroplasty.Orthop Clin North Am. 1998 Jul;29(3):519-33. doi: 10.1016/s0030-5898(05)70026-2. Orthop Clin North Am. 1998. PMID: 9706297 Review.
Cited by
-
[Irreparable rotator cuff tears. Debridement, partial reconstruction, tendon transfer or reversed shoulder arthroplasty].Orthopade. 2016 Feb;45(2):149-58. doi: 10.1007/s00132-015-3204-y. Orthopade. 2016. PMID: 26768144 Review. German.
-
Short-Term Outcomes of the Grammont Reverse Shoulder Arthroplasty: Comparison between First and Second Generation Delta Prosthesis.Joints. 2021 Jun 20;7(4):141-147. doi: 10.1055/s-0041-1731010. eCollection 2019 Dec. Joints. 2021. PMID: 34235377 Free PMC article.
-
[Reversed total shoulder arthroplasty in rotator cuff defect arthropathy].Orthopade. 2018 May;47(5):390-397. doi: 10.1007/s00132-018-3543-6. Orthopade. 2018. PMID: 29516107 Review. German.
-
Convertible-platform shoulder arthroplasty.JSES Rev Rep Tech. 2023 Oct 17;4(3):594-599. doi: 10.1016/j.xrrt.2023.09.010. eCollection 2024 Aug. JSES Rev Rep Tech. 2023. PMID: 39157239 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Treatment strategies for infection after reverse shoulder arthroplasty.Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2014 Jul;24(5):723-31. doi: 10.1007/s00590-013-1251-9. Epub 2013 Jun 8. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2014. PMID: 23748670
References
-
- Bateman JE. The diagnosis and treatment of ruptures of the rotator cuff. Surg Clin North Am. 1963;43:1523–30. - PubMed
-
- Boileau P, Watkinson DJ, Hatzidakis AM, Balg F. Grammont reverse prosthesis: design, rationale and biomechanics. J Shoulder Elbow Surg (Suppl 1) 2001;14:S147–S61. - PubMed
-
- Boileau P, Chuinard C, Le Huec JC, Walch G, Trojani C. Proximale humerus fracture sequelae: impact of a new radiographic classification on arthroplasty. Clin Orthop. 2006a;((442)):121–30. - PubMed
-
- Boileau P, Watkinson D, Hatzidakis AM, Hovorka I. The Grammont reverse shoulder prosthesis: Results in cuff tear arthritis, fracture sequelae and revision arthroplasty. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2006;15:527–40. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
