The identification of the SNARE complex required for the fusion of VLDL-transport vesicle with hepatic cis-Golgi
- PMID: 20450495
- PMCID: PMC4861233
- DOI: 10.1042/BJ20100336
The identification of the SNARE complex required for the fusion of VLDL-transport vesicle with hepatic cis-Golgi
Abstract
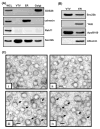
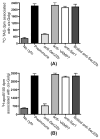
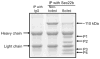
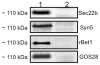
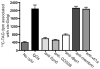
VLDLs (very-low-density lipoproteins) are synthesized in the liver and play an important role in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. Following their biogenesis in hepatic ER (endoplasmic reticulum), nascent VLDLs are exported to the Golgi which is a physiologically regulatable event. We have previously shown that a unique ER-derived vesicle, the VTV (VLDL-transport vesicle), mediates the targeted delivery of VLDL to the Golgi lumen. Because VTVs are different from other ER-derived transport vesicles in their morphology and biochemical composition, we speculated that a distinct set of SNARE (soluble N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor-attachment protein receptor) proteins would form a SNARE complex which would eventually facilitate the docking/fusion of VTVs with Golgi. Our results show that Sec22b is concentrated in VTVs as compared with the ER. Electron microscopic results show that Sec22b co-localizes with p58 and Sar1 on the VTV surface. Pre-treatment of VTV with antibodies against Sec22b inhibited VTV-Golgi fusion, indicating its role as a v-SNARE (vesicle SNARE). To isolate the SNARE complex, we developed an in vitro docking assay in which VTVs were allowed to dock with the Golgi, but fusion was prevented to stabilize the SNARE complex. After the docking reaction, VTV-Golgi complexes were collected, solubilized in 2% Triton X-100 and the SNARE complex was co-immunoprecipitated using anti-Sec22b or GOS28 antibodies. A approximately 110 kDa complex was identified in non-boiled samples that was dissociated upon boiling. The components of the complex were identified as Sec22b, syntaxin 5, rBet1 and GOS28. Antibodies against each SNARE component significantly inhibited VTV-Golgi fusion. We conclude that the SNARE complex required for VTV-Golgi fusion is composed of Sec22b, syntaxin 5, rBet1 and GOS28.
Figures


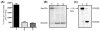
Similar articles
-
CideB protein is required for the biogenesis of very low density lipoprotein (VLDL) transport vesicle.J Biol Chem. 2013 Feb 15;288(7):5157-65. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.434258. Epub 2013 Jan 7. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23297397 Free PMC article.
-
VLDL exits from the endoplasmic reticulum in a specialized vesicle, the VLDL transport vesicle, in rat primary hepatocytes.Biochem J. 2008 Jul 15;413(2):333-42. doi: 10.1042/BJ20071469. Biochem J. 2008. PMID: 18397176
-
The identification of a novel endoplasmic reticulum to Golgi SNARE complex used by the prechylomicron transport vesicle.J Biol Chem. 2006 Jul 28;281(30):20974-20982. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M601401200. Epub 2006 May 30. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 16735505 Free PMC article.
-
Diverse Role of SNARE Protein GS28 in Vesicle Trafficking and Diseases.Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2023;24(4):288-295. doi: 10.2174/1389203724666230315143542. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2023. PMID: 36924089 Review.
-
SNAREs and membrane fusion in the Golgi apparatus.Biochim Biophys Acta. 1998 Aug 14;1404(1-2):9-31. doi: 10.1016/s0167-4889(98)00044-5. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1998. PMID: 9714710 Review.
Cited by
-
CideB protein is required for the biogenesis of very low density lipoprotein (VLDL) transport vesicle.J Biol Chem. 2013 Feb 15;288(7):5157-65. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.434258. Epub 2013 Jan 7. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23297397 Free PMC article.
-
Prolonged fasting elicits increased hepatic triglyceride accumulation in rats born to dexamethasone-treated mothers.Sci Rep. 2017 Sep 4;7(1):10367. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-10642-1. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28871187 Free PMC article.
-
Cathepsin B regulates hepatic lipid metabolism by cleaving liver fatty acid-binding protein.J Biol Chem. 2018 Feb 9;293(6):1910-1923. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M117.778365. Epub 2017 Dec 19. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 29259130 Free PMC article.
-
Positional cloning of a type 2 diabetes quantitative trait locus; tomosyn-2, a negative regulator of insulin secretion.PLoS Genet. 2011 Oct;7(10):e1002323. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002323. Epub 2011 Oct 6. PLoS Genet. 2011. PMID: 21998599 Free PMC article.
-
Nlp-dependent ER-to-Golgi transport.Int J Biol Sci. 2024 May 11;20(8):2881-2903. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.91792. eCollection 2024. Int J Biol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38904019 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shelness GS, Ingram MF, Huang XF, DeLozier JA. Apolipoprotein B in the rough endoplasmic reticulum: translation, translocation and the initiation of lipoprotein assembly. J Nutr. 1999;129:456S–462S. - PubMed
-
- Bakillah A, Nayak N, Saxena U, Medford RM, Hussain MM. Decreased secretion of ApoB follows inhibition of ApoB–MTP binding by a novel antagonist. Biochemistry. 2000;39:4892–4899. - PubMed
-
- Shelness GS, Ledford AS. Evolution and mechanism of apolipoprotein B-containing lipoprotein assembly. Curr Opin Lipidol. 2005;16:325–332. - PubMed
-
- Olofsson SO, Asp L, Boren J. The assembly and secretion of apolipoprotein B-containing lipoproteins. Curr Opin Lipidol. 1999;10:341–346. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

