Sleep in congestive heart failure
- PMID: 20451026
- PMCID: PMC3424608
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mcna.2010.02.009
Sleep in congestive heart failure
Abstract
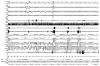
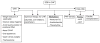
Breathing disorders during sleep are common in congestive heart failure (CHF). Sleep-disordered breathing (SDB) in CHF can be broadly classified as 2 types: central sleep apnea with Cheyne-Stokes breathing, and obstructive sleep apnea. Prevalence of SDB ranges from 47% to 76% in systolic CHF. Treatment of SDB in CHF may include optimization of CHF treatment, positive airway pressure therapy, and other measures such as theophylline, acetazolamide, and cardiac resynchronization therapy. Periodic limb movements are also common in CHF.
Figures

References
-
- Hunt SA, Baker DW, Chin MH, et al. ACC/AHA Guidelines for the evaluation and management of chronic heart failure in the adult: executive summary: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2001;104(24):2996–3007. - PubMed
-
- Levy D, Kenechaiah S, Larson MG, et al. Long-term trends in the incidence of and survival with heart failure. N Engl J Med. 2002;347(18):1397–402. - PubMed
-
- Javaheri S, Parker TJ, Liming JD, et al. Sleep apnea in 81 ambulatory male patients with stable heart failure. Types and their prevalences, consequences, and presentations. Circulation. 1998;97(21):2154–9. - PubMed
-
- Tremel F, Pépin JL, Veale D, et al. High prevalence and persistence of sleep apnoea in patients referred for acute left ventricular failure and medically treated over 2 months. Eur Heart J. 1999;20(16):1201–9. - PubMed
-
- Sin DD, Fitzgerald F, Parker JD, et al. Risk factors for central and obstructive sleep apnea in 450 men and women with congestive heart failure. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1999;160(4):1101–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

