Systematic reduction of cohesin differentially affects chromosome segregation, condensation, and DNA repair
- PMID: 20451387
- PMCID: PMC2892909
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cub.2010.04.018
Systematic reduction of cohesin differentially affects chromosome segregation, condensation, and DNA repair
Abstract
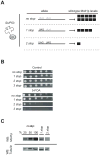
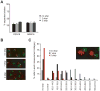
Cohesin's complex distribution on chromosomes and its implication in numerous cellular processes makes it an excellent paradigm for studying the relationship between the in vivo concentration of a protein and its in vivo function. Here, we report a method to generate systematic quantized reductions (QR) in the in vivo concentration of any yeast protein. With QR, we generate strains with 13% and 30% of wild-type levels of the limiting subunit of cohesin, Mcd1p/Scc1p/Rad21p. Reducing cohesin levels reveals a preferential binding of cohesin to pericentric regions over cohesin-associated regions (CAR) on chromosome arms. Chromosome condensation, repetitive DNA stability, and DNA repair are compromised by decreasing cohesin levels to 30% of wild-type levels. In contrast, sister-chromatid cohesion and chromosome segregation are unaffected even when cohesin levels are reduced to 13% of wild-type levels. The requirement for different in vivo cohesin concentrations to achieve distinct cohesin functions provides an explanation for how cohesin mutations can specifically lead to adult disorders such as Cornelia de Lange Syndrome and Roberts Syndrome without compromising the cell divisions needed for development and maturation. Our successful application of QR to cohesin suggests that QR is a powerful tool to study other proteins/pathways with multiple functions.
Copyright 2010 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Onn I, Heidinger-Pauli JM, Guacci V, Unal E, Koshland DE. Sister chromatid cohesion: a simple concept with a complex reality. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2008;24:105–129. - PubMed
-
- Liebman SW, Srodulski Z, Reed CR, Stewart JW, Sherman F, Brennan G. Yeast amber suppressors corresponding to tRNA3Leu genes. J Mol Biol. 1984;178:209–226. - PubMed
-
- Little JW. Mutants of bacteriophage T4 which allow amber mutants of gene 32 to grow in ochre-suppressing hosts. Virology. 1973;53:47–59. - PubMed
-
- Michaelis C, Ciosk R, Nasmyth K. Cohesins: chromosomal proteins that prevent premature separation of sister chromatids. Cell. 1997;91:35–45. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

